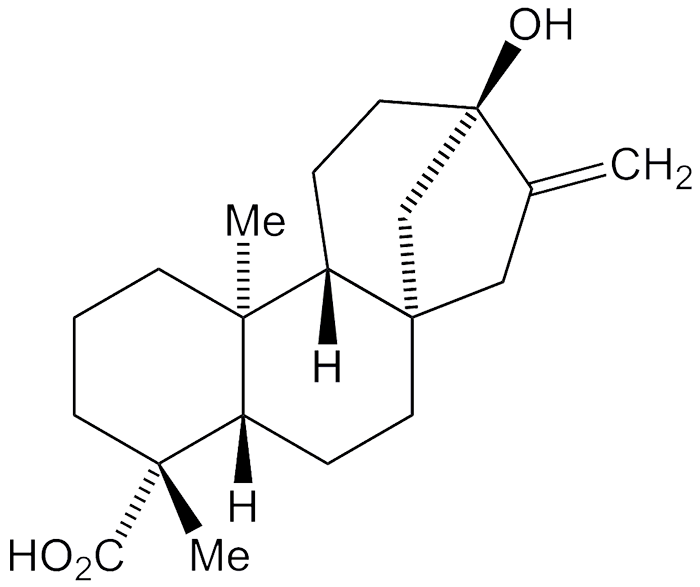
Steviol is a diterpene found in the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana, a member of the sunflower family that is native to Paraguay and Brazil. For centuries, natives of those countries have used its leaves as a sweetener. E. Mosettig and W. R. Nes at the National Institutes of Health (NIH; Bethesda, MD) produced it in the lab using enzymes to hydrolyze its glycoside stevioside in 1955. In the early 1960s, F. Dolder et al. at NIH and H. Vorbrueggen and C. Djerassi at Stanford University determined steviol's structure and stereochemistry.
These days, the product stevia prepared from S. rebaudiana leaves has become popular as a “natural” sweetener in place of such synthetic sweeteners as saccharin, aspartame, and sucralose.
The US Food and Drug Administration banned the import of stevia in 1991 because incomplete toxicology studies did not provide sufficient information on possible harmful effects. It was cleared for some uses in 1995, but not until 2008 did FDA approve a steviol glycoside for use as a sweetener.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

