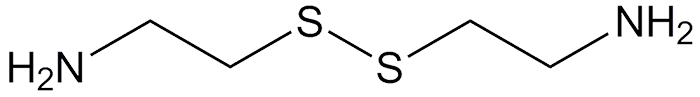
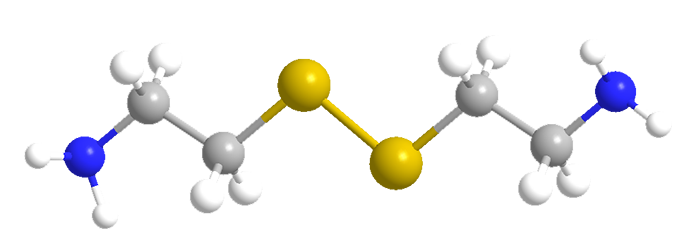
Cystamine is a poisonous, viscous oil that is formed when the amino acid cystine is thermally decarboxylated. C. Neuberg et al. discovered this reaction in 1907 when they attempted to distill cystine. In 1940, in the course of synthesizing vitamin B1-like drugs, E. J. Mills, Jr., and M. T. Bogert synthesized cystamine by oxidizing cysteamine (2-mercaptoethylamine) with H2O2.
Cystamine itself is unstable and cannot be distilled without decomposing. It is usually handled as the dihydrochloride salt. Its uses include derivatizing polymers for analysis by liquid chromatography, cross-linking polymers to make hydrogels, and functionalizing nanoparticles that are used for siRNA and DNA delivery.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

