What molecule am I?
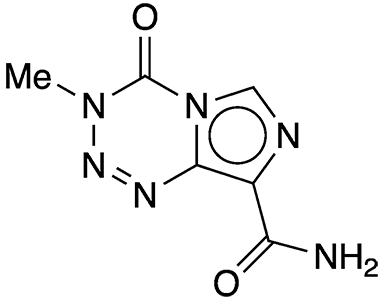
Temozolomide (TMZ) is a chemotherapy drug often used to treat glioblastoma, the most aggressive form of cancer that begins in the brain. This cancer is extremely difficult to treat because it usually recurs even after extensive surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation.
TMZ was developed at Aston University (Birmingham, UK) more than 20 years ago. In 1999, the US Food and Drug Administration granted approval to Merck to market it under the trade name Temodar for treating glioblastoma and refractory anaplastic astrocytoma. It is available in capsule and injectable forms.
TMZ’s mode of action is alkylation, which causes serious side effects such as reduction in blood cells, weakening of the immune system, and secondary cancers. Only a small portion of administered TMZ enters the brain, making most of it free to cause problems in other parts of the body.
Now, Paul J. Hergenrother and colleagues at the University of Illinois (Urbana–Champaign) report that a modification to TMZ’s structure makes it easier for the drug to penetrate the blood–brain barrier. When the team replaced the molecule’s amide group with a methyl ketone group, the percentage of the drug that entered the central nervous system in mice increased from 8% to 69%.
In a mouse model of glioblastoma, treatment with the modified drug (K-TMZ) increased survival indefinitely. The researchers’ next step is to test K-TMZ on larger glioblastoma-affected animals.
Temozolomide hazard information
| GHS classification*: acute toxicity, oral, category 4 | |
| H302—Harmful if swallowed | |
| GHS classification: skin irritation, category 2 | |
| H315—Causes skin irritation | |
| GHS classification: eye irritation, category 2A | |
| H335—May cause respiratory irritation | |
| GHS classification: specific target organ toxicity, single exposure, respiratory tract irritation, category 3 | |
| H335—May cause respiratory irritation | |
| GHS classification: germ cell mutagenicity, category 1B | |
| H340—May cause genetic defects | |
| GHS classification: carcinogenicity, category 1B | |
| H350—May cause cancer | |
| GHS classification: reproductive toxicity, category 1B | |
| H360—May damage fertility or the unborn child | |
*Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals. Explanation of pictograms.
Temozolomide fast facts
| CAS Reg. No. | 85622-93-1 |
| Empirical formula | C6H6N6O2 |
| Molar mass | 194.15 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to light tan or light pink powder |
| Melting point | 212 ºC (dec.) |
| Water solubility | 3.5 g/L |
MOTW update
Propofol was the Molecule of the Week for August 1, 2005. It is a fast-acting intravenous anesthetic notoriously known for its association with the death of Michael Jackson. Recently, scientists in Spain discovered that propofol can be used to disrupt burdensome memories in people with post-traumatic stress disorder or severe phobias. Bryan Strange and his colleagues at the Technical University of Madrid demonstrated their finding by showing subjects disturbing videos, then injecting them with propofol. One day after the individuals awakened from the anesthesia, they had difficulty remembering the traumatic portions of the videos.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

