What molecule am I?
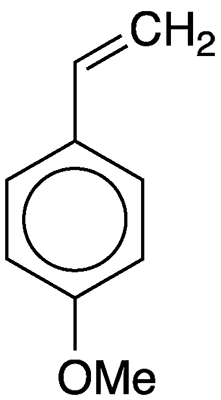
4-Vinylanisole (4VA)—frequently also called 4-methoxystyrene—is a naturally occurring aroma compound. Among other sources, it is one of the volatile components of the French brandy Mirabelle, which is obtained by fermenting the juice of the mirabelle plum (Prunus domestica subsp. syriaca).
Beyond the brandy connection, 4VA is the center of a more spectacular natural phenomenon. This year, Xianhui Wang, Le Kang, and six collaborators at the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Beijing) reported that 4VA is the culprit responsible for locust swarms, such as those that recently devastated large portions of East Africa.
When solitary migratory locusts (Locusta migratoria) form small groups, they begin to emit 4VA, attracting additional insects. As the locusts aggregate, the 4VA signal becomes stronger, and the swarm grows exponentially. This year’s swarm—some call it a “Biblical plague”—covered thousands of square kilometers, mostly in Kenya and Ethiopia, but also in other African and Middle Eastern countries.
4VA’s aggregation pheromone property might have a positive side. Instead of using pesticides to control the locusts, 4VA could potentially be used as a bait to trap the insects before they begin the swarming process, according to Wang, Kang, et al. The researchers also found that a genetic modification prevented locusts from detecting 4VA signals; but others in the field warn against unintended consequences from this sort of alteration.
4-Vinylanisole hazard information
| Hazard class* | Hazard statement | |
|---|---|---|
| Flammable liquids, category 4 | H227—Combustible liquid | |
| Skin corrosion/irritation, category 2 | H315—Causes skin irritation | |
| Serious eye damage/eye irritation, category 2 | H319—Causes serious eye irritation | |
* Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals.
Explanation of pictograms.
MOTW update: February 29, 2024
4-Vinylanisole1 (4VA. aka 4-methoxystyrene) was the Molecule of the Week for November 2, 2020. It is an aroma compound particularly known as a volatile component of a French brandy. In 2020, Chinese researchers reported that 4VA is a locust pheromone that causes the insects to swarm.
This month, Hong Pan, Daoyi Guo, and co-workers at Gannan Normal University (Ganzhou, China) described a de novo biosynthesis of 4VA. They used engineered Escherichia coli as the host organism to synthesize the pheromone from erythrose-4-phosphate2 and phosphoenolpyruvate3. The authors state that their synthetic method is an improvement over current chemical methods for producing 4VA and would increase the supply of the compound for capturing locusts and monitoring their population dynamics.
1. CAS Reg. No. 637-69-4.
2. CAS Reg. No. 138-08-9.
3. CAS Reg. No. 585-18-2.
This molecule was suggested by a reader. We present almost all of the molecules suggested by our readers. If you have a molecule you would like us to consider, please send us a message. And thank you for your interest in Molecule of the Week! —Ed.
4-Vinylanisole fast facts
| CAS Reg. No. | 637-69-4 |
| SciFinder nomenclature | Benzene, 1-ethenyl-4-methoxy- |
| Empirical formula | C9H10O |
| Molar mass | 134.18 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Boiling Point | 205 ºC |
| Water solubility | Insoluble |
A question for readers
Fun fact: 4VA and water have essentially the same density under ambient conditions. What, if anything, are we to make of this? Please send your thoughts to motw@acs.org.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

