What molecules are we?
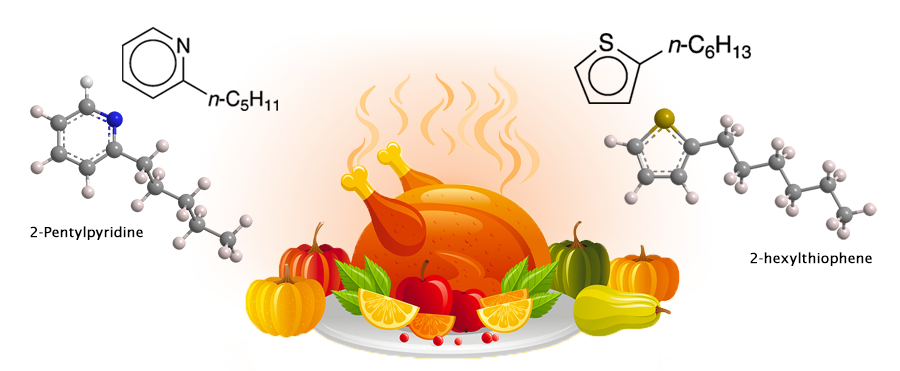
Thanksgiving traditionally means turkey; and turkey means the aromas that waft throughout the house while it’s roasting. But what’s responsible for these delicious smells?
Answer: the Maillard reaction. Discovered by French chemist Louis-Camille Maillard in 1912, the “reaction” is actually a complex series of steps that begins with the interaction between carbonyl groups of open-chain sugars and amine groups of amino acids to form N-aldosylamines. Eventually, depending on the food being heated, the sequence ends with the creation of multiple chemical entities, including many heterocyclic compounds.
These reactions occur when foodstuffs are heated to 140–165 ºC. In addition to the aromas they produce, they are responsible for browning baked, grilled, or roasted foods such as breads, vegetables, and meats. Browning is accelerated in an alkaline environment.
All of which brings us back to turkey. As with other roasted meats, the Maillard reaction produces numerous compounds. Two that have been reported in the literature are 2-pentylpyridine and 2-hexylthiophene, shown here. (No systematic study of all of the Maillard products from turkey appears to have been conducted.)
So, when your host serves you delicious roasted turkey with all the fixings, please compliment her or him on an excellent helping of 2-pentylpyridine and 2-hexylthiophene.
2-Pentylpyridine hazard information
| GHS classification*: flammable liquids, category 4 | |
| H227—Combustible liquid | |
| GHS classification: skin irritation, category 2 | |
| H315—Causes skin irritation | |
| GHS classification: serious eye irritation, category 2A | |
| H319—Causes serious eye irritation | |
| GHS classification: specific target organ toxicity, single exposure; respiratory tract irritation, category 3 | |
| H335—May cause respiratory irritation | |
*Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals. Explanation of pictograms.
2-Hexylthiophene hazard information
| GHS classification: acute toxicity, oral, category 4 | |
| H302—Harmful if swallowed | |
| GHS classification: serious eye irritation, category 2A | |
| H319—Causes serious eye irritation | |
| GHS classification: hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard, category 4 | |
| H413—May cause long-lasting harmful effects to aquatic life | |
2-Pentylpyridine fast facts
| CAS Reg. No. | 2294-76-0 |
| Empirical formula | C10H15N |
| Molar mass | 149.23 |
| Appearance | Colorless to yellow liquid |
| Boiing point | 206–210 ºC |
| Water solubility | ≈1 g/L (est.) |
2-Hexylthiophene fast facts
| CAS Reg. No. | 18794-77-9 |
| Empirical formula | C10H16S |
| Molar mass | 168.30 |
| Appearance | Colorless to pale yellow liquid |
| Boiling point | 228–230 ºC |
| Water solubility | <1 g/L (est.) |

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

