FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE

INDIANAPOLIS, March 26, 2023 — Black women and others with curly or kinky hair encounter a vast and confusing array of haircare options. Advice on the best products to use for a certain type of hair is often contradictory, and the results can be highly variable. Now, scientists are bringing order to this chaos by identifying properties such as the number of curls or coils in a given length of hair that could eventually help users pick the perfect product and achieve consistent results.
The researchers will present their findings today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Spring 2023 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in-person March 26–30, and features more than 10,000 presentations on a wide range of science topics.
“As an African American, I was born with very curly, seemingly unmanageable hair, and other ethnicities can possess similar hair properties,” says Michelle Gaines, Ph.D., the project’s principal investigator. Gaines used to rely on chemical relaxers to straighten her tresses but stopped when she became pregnant. She was then confronted with an overwhelming variety of products available to style and care for natural hair. Limited guidance about the best options for her particular hair type, and conflicting advice from friends, YouTube videos and other resources, didn’t help the situation.
Clearly, Gaines says, there is a major knowledge gap that needs to be closed, so she has set out to fill it. “As a polymer chemist and materials scientist, I thought it would be great to start a project where I could study the nuances of my hair, because I felt like it wasn’t very well understood,” she says.
Most prior research on properties was done on wavy or straight strands from white or Asian people, according to Gaines, who is at Spelman College, a historically Black college for women. Less is known about what has traditionally been called “African” hair, she says, though researchers at Groote Schuur Hospital and the University of Cape Town in South Africa have published some findings.
L’Oréal, as well as celebrity hair stylist Andre Walker and others, have developed systems to classify different types of hair. Walker’s system ranges from straight to kinky, a category including tight coils and zig-zag strands with angular bends. Although some people believe all of these classification methods convey a preference for a smoother and straighter appearance — a bias with historic links to the preferential treatment of enslaved people who had straighter hair and lighter skin — they’re intended to help users choose the most suitable haircare products. Gaines felt these systems worked well for straight and wavy hair but lacked the nuance to distinguish the many varieties of curly and kinky hair.
Gaines wanted to see if she could identify differences in properties other than curl shape and tightness, and then use those differences to develop a more precise and quantitative classification system. Undergraduates at Spelman eagerly lined up to help. Gaines and her student, Imani Page, are collaborating with Alfred Crosby, Ph.D., and Gregory Grason, Ph.D., at the University of Massachusetts Amherst; their expertise includes material property characterization and modeling of complex materials and soft matter.
View larger image
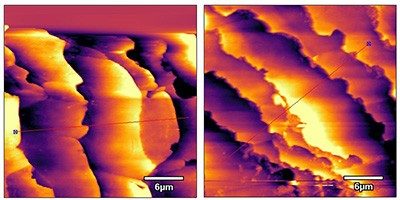
The team measured the mechanical properties of wavy, curly and kinky hairs with a texture analyzer and a dynamic mechanical analyzer. These instruments measure force, stress and other parameters as a strand is first uncurled and then stretched until it breaks.
Among other findings, the team recently reported results for the “stretch ratio,” a new parameter they developed to quantify and compare the force required to uncurl a strand until it’s straight. That ratio was found to be negligible for straight hair (since it can’t be uncurled), about 0.8 for wavy, 1.1 for kinky and 1.4 for curly. This measurement could therefore be used as an indicator of the initial curliness of a sample, providing a quantifiable way to distinguish between these types.
The team also measured geometric properties, such as the diameter, cross section and 3D shape of strands, using optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and a camera. In addition, the researchers developed new parameters, including the number of complete waves, curls or coils — known as contours — that they measured on 3-cm lengths of hair. They found that wavy hair has less than one full contour in that length, curly has about two, and kinky/coily has approximately three or more. The results suggest that people will be able to classify their own hair by counting contours, Gaines says.
In the latest work, Gaines has begun examining the layer that protects the surface of each hair fiber. Known as the cuticle, it consists of flat cells that overlap each other, like roof shingles. Cuticles have a natural tendency to open and close reversibly when exposed to water, shampoo and conditioner. However, excessive acid and moisture retention can cause permanent damage to the cuticles, causing them to remain irreversibly lifted, thus exposing the inner cortex of the hair fiber. Irreversibly lifted cuticles, and cuticles that easily open and close, make the strand more porous, which causes more moisture absorption. Gaines’ preliminary findings show the cuticle layers are larger and spaced further apart in wavy hair than in curly and coily hair. Also, the cuticle edges are smoother in wavy hair. These findings could help the researchers explain why curly and coily locks dry out faster than wavy and straight tresses. Ultimately, Gaines hopes, the team’s findings will identify the best parameters for developers to design and for consumers to select the most suitable products for each of the wondrously varied categories of hair.
The researchers acknowledge support from the University of Massachusetts Amherst.
A recorded media briefing on this topic will be posted Monday, March 27, by 10 a.m. Eastern time at www.acs.org/acsspring2023briefings. Reporters can request access to media briefings during the embargo period by contacting newsroom@acs.org.
For health and safety information for ACS Spring 2023, please visit the FAQ webpage.
###
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive press releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note: ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies.

