FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
“Natural Coumarin Isomers with Dramatically Different AIE Properties: Mechanism and Application”
ACS Central Science

Plants that glow under ultraviolet (UV) light aren’t only a figment of science fiction TV and movies. Roots of a traditional medicine plant called the orange climber, or Toddalia asiatica, can fluoresce an ethereal blue hue. And now, researchers in ACS Central Science have identified two coumarin molecules that could be responsible. These natural coumarins have unique fluorescent properties, and one of the compounds could someday be used for medical imaging.
Fluorescent substances take in UV light that’s directed on them and release vibrantly colored visible light. And some glow even more brightly when they are close together, a phenomenon seen in compounds called aggregation-induced emission luminogens (AIEgens). They are key components in some optical devices, cellular imaging techniques and environmental sensors. However, these molecules are usually made in a lab, and many are toxic. Some plants already have this ability, so, Ben Zhong Tang, Zheng Zhao, Xiao-Dong Luo and colleagues turned to nature to find naturally occurring and safer AIEgens.
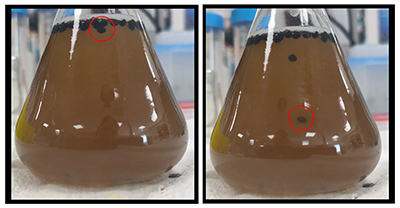
The researchers dried orange climber roots, crushed them into a powder, and then isolated and identified coumarin compounds with aggregation-induced emission properties: 5-methoxyseselin (5-MOS) and 6-methoxyseselin (6-MOS). When dissolved in an organic solvent, 5-MOS exhibited a blue-green glow and 6-MOS had a slightly dimmer blue glow. In addition, both AIEgens had low cytotoxicity and good biocompatibility. Then in a final series of experiments, the team found that mitochondria could be clearly identified in live cells stained with 5-MOS without any additional processing, making cell imaging easier and faster than with most current methods. The newly reported compound is a natural, plant-derived option that could advance bioimaging, the researchers say.
The authors acknowledge funding from the High-level Talent Promotion and Training Project of Kunming; Project of Yunnan Characteristic Plant Screening and R&D Service CXO Platform; Science, Technology and Innovation Commission of Shenzhen Municipality; Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Functional Aggregate Materials; the Research Grants Council of Hong Kong; the Innovation and Technology Commission; the Open Fund of Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Luminescence from Molecular Aggregates; and South China University of Technology; and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation.
###
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive press releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note: ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies.