Lesson Overview for Teachers
View the video below to see what you and your students will do in this lesson.
Objective
Students will be able to explain that if two substances cause turn a pH indicator different colors, they must be different substances. Students will be able to explain that the color that a substance turns a pH indicator is a characteristic property of that substance. Students will also be able to explain that different substances react in characteristic ways that can be used to identify a substance.
Key Concepts
- A pH or acid-base indicator is a compound that changes color depending on the pH of the substance that is added to it.
- Acids and bases make pH indicators turn different colors.
- Two substances that turn the same pH indicator different colors must be different substances.
- The color that a substance turns a pH indicator is a characteristic property of that substance.
- An acid can neutralize a base, and a base can neutralize an acid
NGSS Alignment
- NGSS 5-PS1-3: Make observations and measurements to identify materials based on their properties.
- NGSS 5-PS1-4: Conduct an investigation to determine whether the mixing of two or more substances results in new substances.
Summary
- Students squeeze red cabbage leaves in water to make an acid-base indicator solution.
- Students add laundry detergent powder (a base) and cream of tartar (an acid) to the indicator and see that the two solids cause different color changes.
- Students recognize that a particular color change is a characteristic property of a substance and that a color change can also be used as evidence that a chemical reaction has occurred.
- Students will explore what happens during neutralization by using a base to neutralize an acid, and an acid to neutralize a base.
Evaluation
Download the student activity sheet (PDF) and distribute one per student when specified in the activity. The activity sheet will serve as the Evaluate component of the 5-E lesson plan.
Safety
Make sure you and your students wear properly fitting safety goggles. Most generic or all-purpose solid laundry detergents contain 20–30% sodium carbonate by weight and may cause skin burns and eye irritation. The detergent powder may also be harmful if swallowed or inhaled. Avoid contact of laundry detergent powder with eyes and skin. Do not handle the powder with bare hands.
Clean-up and Disposal
Remind students to wash their hands after completing the activity. All common household or classroom materials can be saved or disposed of in the usual manner.
Materials
Materials needed for each group
- Red cabbage leaves
- Cream of tartar
- Powdered laundry detergent
- Water
- Zip-closing plastic bag (storage-grade, quart-size)
- 5 Clear plastic cups
- 2 Small cups
- 2 Popsicle sticks
- 1 Tablespoon
- Permanent marker
- White piece of paper
- Measuring spoon (for Teacher Preparation)
Materials needed for each group
- Water
- Epsom salt
- 1 piece of Ivory soap
- Paper towel
- 2 Popsicle sticks
- 2 Empty 8-oz disposable water bottles with lids
- 4 Clear plastic cups
- 1 Small cup
- 1 Tablespoon
- 1 Teaspoon
Notes about the materials
Be sure you and the students wear properly fitting goggles.
Use a fresh red cabbage (pre-shredded red cabbage will not work well). If you don't use all of your cabbage leaves, you can refrigerate the unused portions and save them for future use.
Teacher Preparation
Label two small cups Cream of Tartar and Detergent for each group.
Place ¼ teaspoon of detergent and ¼ teaspoon of cream of tartar in their labeled cups.
Activity sheet
Download the student activity sheet (PDF) and distribute one per student when specified in the activity.
Engage
1. Introduce the activity and guide the class in making a red cabbage indicator solution.
Tell students that they will use a special color-changing solution, called an indicator, to test two different substances. Explain that they will prepare their own indicator solution using red cabbage leaves and will then test the indicator by adding two different substances to it.
Demonstrate the procedure for preparing an indicator as you guide students to make their own.

Procedure
- Tear 2 red cabbage leaves into small pieces and place them in a storage grade zip-closing plastic bag.
- Carefully add 1 cup of room-temperature water to the plastic bag. Get as much air out of the bag as possible and then seal the bag securely.
- While holding the bag, squeeze the mixture of water and cabbage leaves until the water turns a medium to dark blue. It should take about 3–5 minutes.

- Open a corner of the plastic bag and carefully pour the liquid into an empty, clear plastic cup, leaving the cabbage pieces behind in the bag. The liquid is your indicator solution.
Explain to students that a red cabbage indicator changes color when certain chemicals are added to it. It turns pinkish when acids are added to it and greenish when bases are added to it. The indicator solution remains blue when neutral substances are added to it. A neutral substance is neither an acid nor a base.
Give each student an Activity Sheet (PDF).
Students will record their observations and answer questions about the activity on the activity sheet.
2. Have students add an acid and a base to the indicator.
Question to investigate: What can the color of an indicator solution tell you about the substances added to it?
Procedure
- Label three empty clear plastic cups Indicator + Detergent, Indicator + Cream of Tartar, and Control.
- Carefully pour 2 tablespoons of indicator solution into each cup. Place the three labeled cups on a piece of white paper to make it easier to compare any color changes that are observed.
- Record the color of the indicator solution in the Control cup.
- Use the end of a popsicle stick to scoop up a small amount of cream of tartar. Add the cream of tartar to the Indicator + Cream of Tartar cup.
- Gently swirl the cup to mix. Observe the color of the indicator and record any color change(s) in the chart on the activity sheet.
Expected results
Cream of tartar turns the indicator a pinkish color.
- Use the end of the other popsicle stick to scoop up a small amount of laundry detergent. Add the detergent to the Indicator + Detergent cup.
- Gently swirl the cup to mix. Observe the color of the indicator and record any color change(s) in the chart.
Expected results
Laundry detergent turns the indicator a greenish-blue color.



3. Discuss student observations.
Remind students that a red cabbage indicator turns pink when acids are added to it and green when bases are added to it. Ask students which substance they tested is an acid and which is a base. They should conclude that cream of tartar is an acid and laundry detergent is a base.
4. Have students neutralize the Indicator + Cream of Tartar solution and the Indicator + Laundry detergent solution.
Question to investigate: What happens if you add some acid to the indicator that already contains a base? And what happens if you add some base to the indicator that already contains an acid?

Procedure
- Use the popsicle stick you used for the laundry detergent to add a small amount of detergent to the Indicator + Cream of Tartar cup and gently swirl the cup to mix. Observe and record any color changes.
- If needed, continue adding small amounts of laundry detergent until the solution returns to the original blue color of the indicator in the Control cup.
Expected results
The pink color of the Indicator + Cream of Tartar solution will return to blue after small amounts of laundry detergent are added to it. The color of the indicator may not return to the exact same shade of blue as the control.

- Use the popsicle stick you used for cream of tartar to add a small amount of cream of tartar to the Indicator + Detergent cup and gently swirl the cup to mix. Observe and record any color changes.
- If needed, continue adding small amounts of cream of tartar until the solution returns to the original blue color of the indicator in the Control cup.
Expected results:
The green color of the Indicator + Laundry Detergent solution will return to blue after small amounts of cream of tartar are added to it. The color of the indicator may not return to the exact same shade of blue as the control.
Explain that adding a base to a solution that already has an acid in it is called neutralizing the acid. Adding an acid to a solution that already has a base in it is called neutralizing the base.
Ask students:
- Were you able to return the pink (acidic) and green (basic) indicator solutions back to blue (the control color)?
Yes. - What could you have done if you had added too much detergent to the pink indicator solution and the indicator had turned more green instead of blue?
Adding a very small amount of cream of tartar could turn the solution back to the blue (control) color. - What could you have done if you had added too much cream of tartar to the basic indicator solution and it had turned pink or purplish-pink instead of blue?
Adding a very small amount of detergent could turn the solution back to the blue (control) color.
Explain
5. Show an animation of acids and bases causing an indicator to change color.
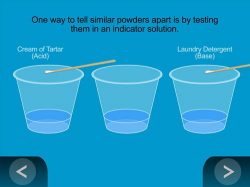
Show the animation Testing Powders with an Indicator Solution.
Explain that acids and bases are like chemical opposites. An acid gives a proton to the indicator. This changes the structure of the indicator, which also causes it to change color. A base accepts a proton from the indicator. This changes the structure of the indicator, which also causes it to change color.
Extend
6. Show students some examples (PDF) of using acids and bases and neutralization.
The color of many hydrangea flowers are dependent on whether the soil in which they are grown are more acidic or more basic.
Excess stomach acid can cause a stomachache. The extra acid can be neutralized by taking an antacid tablet, such as Tums or Rolaids. These antacids contain calcium carbonate, which is a base, and neutralizes the excess acid.
The amount of acid or base in a swimming pool or aquarium can be adjusted by adding either an acid or base to help neutralize the water.
The yellow scale on the left shows the amount of chlorine in the water. This test for chlorine is not a pH test but the reddish color on the right is a pH indicator, which shows the how acidic or basic the water is.


hydrangea in acidic soil (right)