What molecule am I?

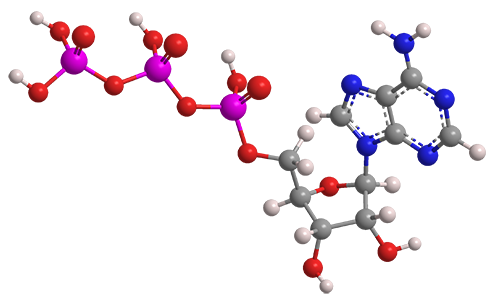
Adenosine 5′-triphosphate, abbreviated ATP and usually expressed without the 5′-, is an important “energy molecule” found in all life forms. Specifically, it is a coenzyme that works with enzymes such as ATP triphosphatase to transfer energy to cells by releasing its phosphate groups. The molecule consists of three components: an adenine bicyclic system, a furanose ring, and a triphosphate chain.
Two research groups reported the discovery of ATP in 1929. Cyrus H. Fiske and Yellapragada Subbarow at Harvard Medical School (Boston) isolated it from mammalian muscle and liver. Likewise, Karl Lohmann at the Kaiser Wilhelm Institutes (Berlin and Heidelberg) identified it in muscle tissues.
ATP isolation from other sources followed over the next 15 years. Koscak Maruyama at Chiba University (Japan) wrote a comprehensive review of the discovery and structure elucidation of ATP in 1987.
ATP is biosynthesized in several ways, as described by Biology Dictionary:
Photophosphorylation is a method specific to plants and cyanobacteria. It is the creation of ATP from ADP using energy from sunlight, and occurs during photosynthesis. ATP is also formed from the process of cellular respiration in the mitochondria of a cell. This can be through aerobic respiration, which requires oxygen, or anaerobic respiration, which does not. Aerobic respiration produces ATP (along with carbon dioxide and water) from glucose and oxygen. Anaerobic respiration uses chemicals other than oxygen, and this process is primarily used by archaea and bacteria that live in anaerobic environments. Fermentation is another way of producing ATP that does not require oxygen; it is different from anaerobic respiration because it does not use an electron transport chain. Yeast and bacteria are examples of organisms that use fermentation to generate ATP.
ATP synthesized in mitochondria is the primary energy source for important biological functions, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and protein synthesis. According to Susanna Törnroth-Horsefield and Richard Neutze at the University of Gothenburg (Göteborg, Sweden), “On any given day you turn over your body weight equivalent in ATP, the principal energy currency of the cell.”
Adenosine triphosphate hazard information
| Hazard class* | Hazard statement |
|---|---|
| Not a hazardous substance or mixture |
*Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals.
MOTW update: January 22, 2024
Adenosine triphosphate1 (ATP) is one of the most important biomolecules because it works with the enzyme ATP triphosphatase to transfer energy to the cells of all life forms.
ATP was discovered in 1929, and 95 years later scientists are still learning about it. This month, Divya Kota, Ramesh Prasad, and Huan-Xiang Zhou* at the University of Illinois Chicago reported that ATP mediates phase separation of basic intrinsically disordered proteins by bridging intermolecular interaction networks. The authors state that highly concentrated ATP droplets “have some of the lowest interfacial tension (≈25 pN/μm) but high zero-shear viscosities (1–15 Pa∙s) due to the bridged protein networks, and yet their fusion has some of the highest speeds (≈1 μm/ms).”
1. CAS Reg. No. 56-65-5.
This molecule was suggested by a reader. We present almost all of the molecules suggested by our readers. If you have a molecule you would like us to consider, please send us a message. And thank you for your interest in Molecule of the Week! —Ed.
Adenosine triphosphate fast facts
| CAS Reg. No. | 56-65-5 |
| SciFinder nomenclature | Adenosine 5′-(tetrahydrogen triphosphate) |
| Empirical formula | C10H16N5O13P3 |
| Molar mass | 507.18 g/mol |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Melting point | 176 ºC |
| Water solubility | ≈1 kg/L |

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

