What molecule am I?
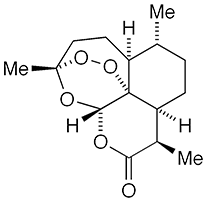
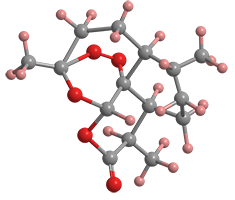
Artemisinin1 is a sesquiterpene endoperoxide/δ-lactone drug for treating malaria caused by the protozoan Plasmodium falciparum. Artemisinin also refers to the group of the molecule’s derivatives.
In 1972, Youyou Tu at the Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine2 (Beijing) discovered artemisinin in the herb Artemisia annua (sweet wormwood), which Is used in traditional Chinese medicine. Tu, who does not have a medical degree, shared the 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for her breakthrough malaria drug.
In 1979, Tu and her co-workers published an article in a Chinese journal on the structure and reactions of artemisinin (which was then called arteannuin), along with the derivative arteannuin B3. Since then, more than 120 additional derivatives have been discovered or synthesized.
Medical researchers have explored the possibilities of using artemisinin against other diseases, including helminthiasis (a parasitic worm infection), cancer, and autoimmune diseases. Just this February, Jing Luo, Qing-wen Tao, and colleagues at China–Japan Friendship Hospital (Beijing) described the mechanisms with which artemisinin combats primary Sjögren’s syndrome, a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the salivary and lachrymal glands, causing dry mouth, dry eye, and fatigue. The researchers found that artemisinin works by modulating the balance of regulatory T cells (Tregs cells) and certain T helper cells (Th17 cells).
For additional information about artemisinins, see the chapter Artemisinin Chemical Research in Artemisinin-Based and Other Antimalarials (2018).
1. CA Index name 3,12-epoxy-12H-pyrano[4,3-j]-1,2-benzodioxepin-10(3H)-one, octahydro-3,6,9-trimethyl-, (3R,5aS,6R,8aS,9R,12S,12aR)-.
2. Now the China Academy of Traditional Chinese Medical Sciences.
3. CAS Reg. No. 50906-56-4.
This was also a Molecule of the Week in 2005.
Artemisinin hazard information*
| Hazard class** | GHS code and hazard statement | |
|---|---|---|
| Organic peroxides, type E | H242—Heating may cause a fire | |
| Serious eye damage/eye irritation, category 2A | H319—Causes serious eye irritation | |
| Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure, respiratory tract irritation, category 3 | H335—May cause respiratory irritation | |
| Short-term (acute) aquatic hazard, category 1 | H400—Very toxic to aquatic life | |
| Long-term (chronic) aquatic hazard, category 1 | H410—Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects | |
*Compilation of multiple safety data sheets; in each class, the most hazardous category is shown.
**Globally Harmonized System (GHS) of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals. Explanation of pictograms.
This molecule was suggested by a reader.
Elafibranor1 is a medication under development by Genfit (Lille, France), a company headed by Jean-François Mouney, who cofounded it in 1999. The drug is intended to treat diabetes (including insulin resistance), dyslipidemia (abnormal blood lipid concentrations), and metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (previously called nonalcoholic fatty liver disease).
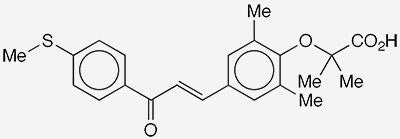
A 2004 international patent application, WO/2004/005243, to Genfit on substituted 1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one derivatives was the original one to cover elafibranor. This was followed in 2007 by US application 2007/00325432. Last month, international application WO/2024/040132 to the US Department of Health and Human Services described combinations of interleukins with elafibranor and other medications as improved cancer treatments.
1. CAS Reg. No. 923978-27-2.
2. Now US Patent 9,221,751 (2015).
Molecule of the Future
Once a month we bring you a newly discovered or developed molecule that has important implications for the future of chemistry or society in general. Look for it the third week of each month. Learn more about this month's Molecule of the Future.
We're looking for more molecules of the future!
Do you have a suggestion for the next molecule of the future? Send your idea to MOTW.
This molecule was suggested by a reader. We present almost all of the molecules suggested by our readers. If you have a molecule that you would like us to consider, please send us a message, preferably including links to references about your suggested molecule. And thank you for your interest in Molecule of the Week! —Ed.
Artemisinin fast facts
| CAS Reg. No. | 63968-64-9 |
| Empirical formula | C15H22O5 |
| Molar mass | 282.34 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals or white powder |
| Melting point | 156–157 °C |
| Water solubility | 28 g/L |

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.


