
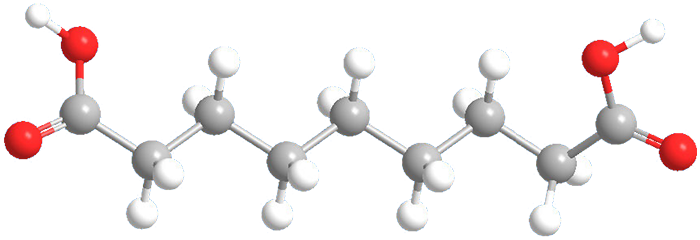
Azelaic acid, formally nonanedioic acid, is a white crystalline solid with a melting point of 106.5 °C. It occurs naturally in grains such as wheat, rye, and barley and is produced industrially by ozonolyzing oleic acid. It is used topically to treat acne and rosacea. Some plants release azelaic acid as a "distress flare" to signal cells to activate their defenses against attacking pathogens.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

