What molecule am I?

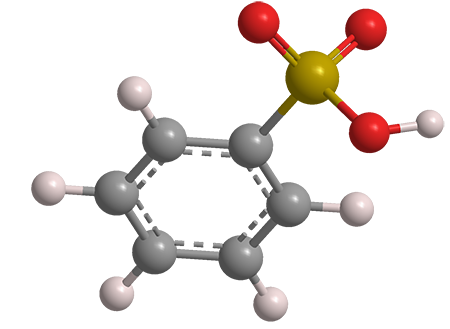
Benzenesulfonic acid is the simplest aromatic sulfonic acid. It is highly water-soluble and a strong acid with a pKa of –2.8. It has been known since at least the 1880s; its synthesis, which goes back to 1916, is via the reaction of benzene with hot concentrated sulfuric acid.
Benzenesulfonic acid is used to produce phenol by fusing it with sodium hydroxide or hydrolyzing one of its salts, usually sodium. Other uses include surfactants made with its metal or amine salts and as a counterion for cationic pharmaceuticals.
For additional information on benzenesulfonic acid’s properties and uses, see articles curated by ScienceDirect.
Benzenesulfonic acid hazard information*
| Hazard class** | GHS code and hazard statement | |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosive to metals, category 1 | H290—May be corrosive to metals | |
| Acute toxicity, oral, category 4 | H302—Harmful if swallowed | |
| Skin corrosion/irritation, category 1C | H314—Causes severe skin burns and eye damage | |
| Serious eye damage/eye irritation, category 1 | H318—Causes serious eye damage | |
| Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure, respiratory tract irritation, category 3 | H335—May cause respiratory irritation | |
*Compilation of multiple safety data sheets.
**Globally Harmonized System (GHS) of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals. Explanation of pictograms.
Molecules from the journals
Cerium(IV) oxide1 (CeO2), also called ceric oxide or ceria, is a rare earth oxide that appears as pale yellow crystals or powder. It occurs in nature mixed with other cerium oxides and as oxides of other rare earth. Its several uses include polishing and decolorizing glass, inclusion in various types of coatings, and catalyzing organic reactions.
This past March, Pinxian Xi and co-workers at Lanzhou University (China) reported a new catalytic application of CeO2. They used it in combination with bismuth trisulfide2 (Bi2S3) to promote the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide to the formate anion. Bi2S3 and CeO2 combine to form a Bi–O–Ce structure, which promotes electron transfer between the two compounds and increases the selectivity of the reaction in favor of formate.
Wickerol A3 and wickerol B4 are triterpenes produced by the soil fungus Trichoderma atroviride that is found worldwide. In 2012, Satoshi Ōmura, Kazuro Shiomi, and co-workers at Kitasato University (Tokyo) reported that the wickerols show potent activity against an influenza virus strain, with the A compound having greater activity than B. In March, Christopher D. Vanderwal and co-workers at the University of California, Irvine, described the enantioselective total syntheses of the two wickerols starting from 2-cyclohexen-1-one5.
1. CAS Reg. No. 1306-38-3.
2. CAS Reg. No. 1345-07-9.
3. CAS Reg. No. 1187951-84-3.
4. CAS Reg. No. 1355394-77-2.
5. CAS Reg. No. 930-68-7.
Molecules from the Journals
MOTW briefly describes noteworthy molecules that appeared in recent ACS journal articles. See this week's
edition below.
This molecule was suggested by a reader. We present almost all of the molecules suggested by our readers. If you have a molecule you would like us to consider, please send us a message. And thank you for your interest in Molecule of the Week! —Ed.
Benzenesulfonic acid
fast facts
| CAS Reg. No. | 98-11-3 |
| SciFinder nomenclature | Benzenesulfonic acid |
| Empirical formula | C6H6O3S |
| Molar mass | 158.18 g/mol |
| Appearance | Deliquescent white crystals or waxy solid |
| Melting point | 65 °Ca |
| Water solubility | 930 g/L (25 °C) |
a. Uncertain; also reported as low as 43 °C.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

