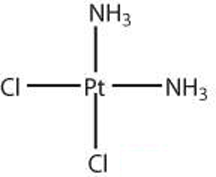
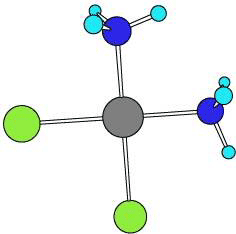
Cisplatin was first identified in 1845; it was originally of interest during the development of coordination theory. At that time, it was called Peyrone’s salt or Peyrone’s chloride, after its discoverer, Michel Peyrone. In the mid-1960s, Cisplatin’s antitumor activity was demonstrated, and it has served as the gold standard (should that be “platinum standard”?) against which newer drugs are compared. Cisplatin is probably best known for its role in helping Tour de France winner Lance Armstrong fight testicular cancer. The trans isomer does not exhibit a similar pharmacological effect.
Related Article: "Sound Science", Chemical & Engineering News, April 7, 2014

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

