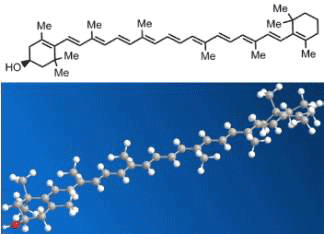
Cryptoxanthin is one of a class of carotenoids called xanthophylls. Its structure is identical to that of β-carotene except that it has a hydroxyl group. Like carotene, it is converted to vitamin A in the human body and acts as an antioxidant. Xanthophylls (from Greek xanthos, yellow) are found in leaves and flowers; when the chlorophyll in leaves is denatured by cold weather, xanthophylls are responsible for leaves’ changing to yellow and red colors.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

