What molecule am I?
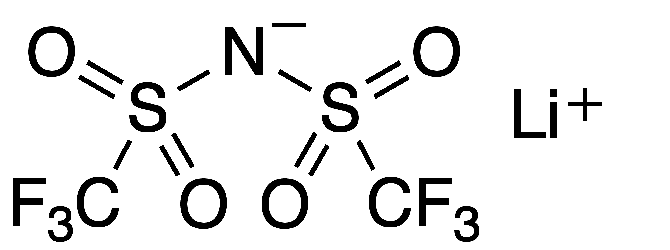
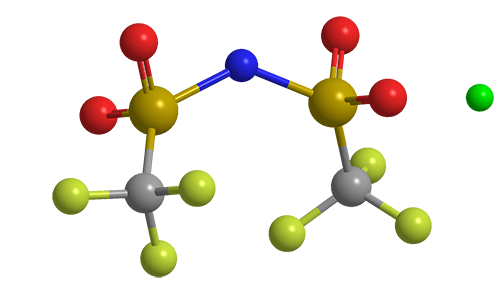
Lithium bis(trifluoromethane)sulfonimide (LiTFSI) is a hydrophilic organic salt that has many uses in electric and electronic systems. Its bis(trifluoromethane)sulfonimide anion, often referred to as bistriflimide, has the useful property of coordinating weakly with cations.
LiTFSI ‘s other important property is its extremely high solubility in water: 21 molal or ≈6 kg/L of solution. Because of its solubility, it has been explored as an electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries, solar cells, and similar applications since at least the late 1980s. LiTFSI is a safer material than the formerly used salt, lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6).
In a 2021 Nature article, André D. Taylor at New York University (New York City) and Yale University (New Haven, CT) and 18 colleagues there and at other institutions in the United States and the Republic of Korea reported a refinement in the use of LiTFSI in solar cells.
Photovoltaic cells made of inexpensive light-absorbing perovskites that have high power-conversion efficiencies have been developed over the past several years. To improve the cells’ ability to transport electrical charges, they are doped with a combination of LiTFSI and a semiconductor called Spiro-OMeTAD1; but this process is extremely slow.
Taylor and his fellow researchers solved the problem by bubbling carbon dioxide into a solution of spiro-OMeTAD and LiTFSI while irradiating the mixture with ultraviolet light. They then cast a film made from the solution onto the perovskite light absorber. The process can be completed in ≈1 min, compared with the older, hours-long doping procedure.
The authors state, “The CO2-treated interlayer exhibits approximately 100 times higher conductivity than a pristine [untreated] film while realizing stable, high-efficiency solar cells without any post-treatments.” They also report that their method is useful for doping π-conjugated polymers.
1. 2,2′,7,7′-Tetrakis[N,N-di(4-methoxyphenyl)amino]-9,9-spirobifluorene, CAS Reg. No. 207739-72-8.
Lithium bis(trifluoromethane)sulfonimide
hazard information*
| Hazard class** | GHS code and hazard statement | |
|---|---|---|
| Acute toxicity, oral, category 3 | H301—Toxic if swallowed | |
| Acute toxicity, dermal , category 3 | H311—Toxic in contact with skin | |
| Skin corrosion/irritation, category 1B | H314—Causes severe skin burns and eye damage | |
| Serious eye damage/eye irritation, category 1 | H318—Causes serious eye damage | |
| Specific target organ toxicity (nervous system), repeated exposure, oral, category 2 | H373—May cause damage to nervous system through prolonged or repeated exposure if swallowed | |
| Short-term (acute) aquatic hazard, category 3 | H402 —Harmful to aquatic life | |
| Long-term (chronic) aquatic hazard, category 3 | H412—Harmful to aquatic life with long-lasting effects | |
*Compilation of selected safety data sheets.
**Globally Harmonized System (GHS) of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals. Explanation of pictograms.
Lithium bis (trifluoromethane) sulfonimide fast facts
| CAS Reg. No. | 90076-65-6 |
| SciFinder nomenclature | Methanesulfonamide, 1,1,1-trifluoro-N-[(trifluoromethyl) sulfonyl]-, lithium salt (1:1) |
| Empirical formula | C2F6LiNO4S2 |
| Molar mass | 287.09 g/mol |
| Appearance | Hygroscopic white powder |
| Melting point | 234–238 °C |
| Water solubility | ≈6 kg/L |

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

