What molecule am I?
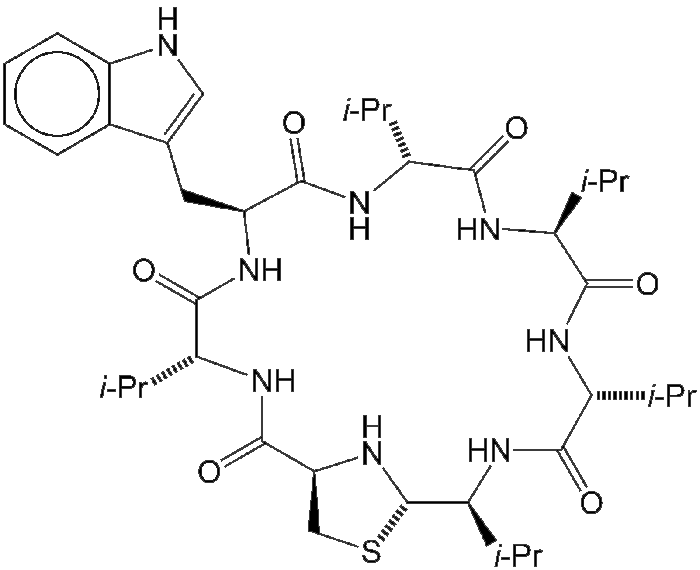

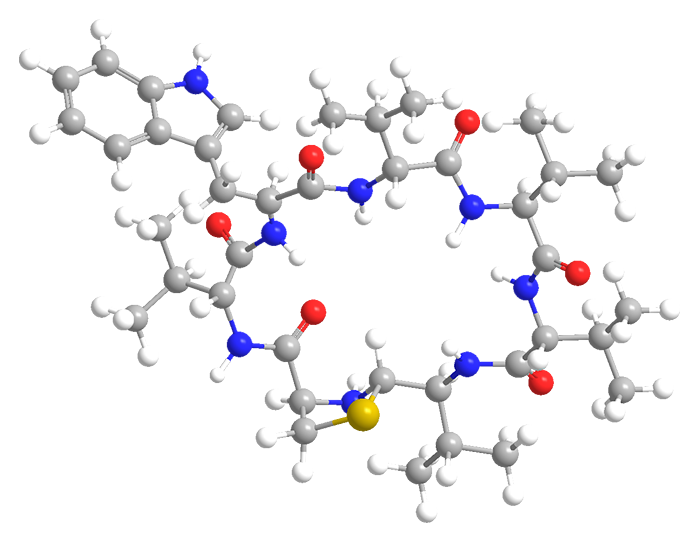
Lugdunin is a 21-membered cyclic peptide that consists of 6 amino acid residues plus a thiazolidine moiety. Five of the amino acids are L-valine and the sixth is L-tryptophan.
This past year, Andreas Peschel, Bernhard Krismer, and colleagues at the University of Tübingen (Germany) and the German Center for Infection Research (Tübingen) discovered that a bacterium that resides in the human nose combats disease-causing Staphylococcus aureus. The bacterium, S. lugdunensis, produces the natural antimicrobial lugdunin.
The discovery of lugdunin explains why not all people infected by S. aureus get sick. In laboratory experiments, the macrocyclic antibiotic even killed methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant enterococci.
Scientists believe that the human body contains other bacteria that produce antimicrobials. The hunt is on!

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

