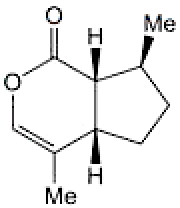
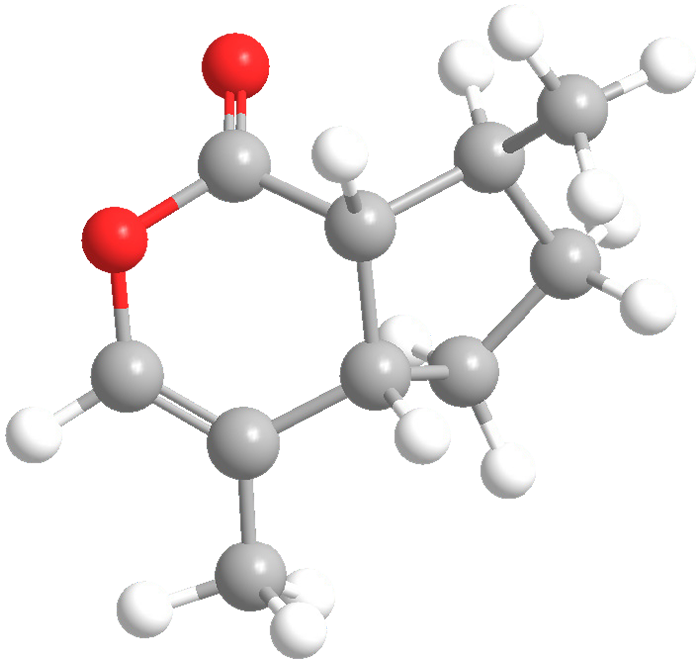
(+)-cis,trans-Nepetalactone is the primary psychoactive ingredient in catnip (Nepeta cataria). It was isolated in 1941 by S. M. McElvain and co-workers at the University of Wisconsin (Madison). It was the first fully characterized methylcyclopentane monoterpenoid. In 2009, M. Christmann and coauthors used cis,trans-nepetalactone as the starting material to synthesize (+)-englerin A, a promising kidney cancer drug candidate. The synthesis confirmed the absolute configuration of natural englerin A.
MOTW update:
May 3, 2021
cis,trans-Nepetalactone is the primary psychoactive ingredient in catnip (Nepeta cataria). In 2009, it was the starting material for synthesizing (+)-englerin A, a promising kidney cancer drug candidate.
It has long been known that catnip repels mosquitoes; but until this year, the repellence mechanism was unknown. Marcus Stensmyr and co-workers at Lund University (Sweden) discovered that nepetalactone activates a receptor in mosquitoes that makes them feel pain. Cats, among many other animals, have the same receptor; but clearly the effect is different for them.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

