
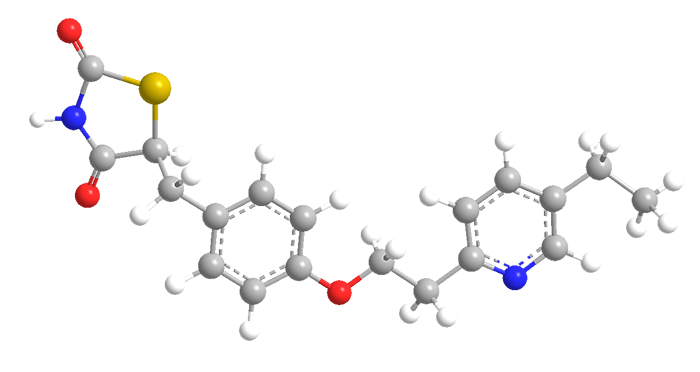
Pioglitazone is a thiazolinedione drug that reduces blood glucose levels in diabetic patients. Takeda Pharmaceuticals launched it under the trade name Actos in 1999. Within 10 years, it became the world’s best-selling diabetes drug. Although it is relatively safe, some countries have stopped its sale because it is associated with bladder tumors.
As indicated in the images, pioglitazone is a racemic mixture of two enantiomers. Because the enantiomers interconvert in vivo, no differences are seen between the two in terms of pharmacological activity.
In 2015, Stéphane Prost, Philippe Leboulch, and colleagues at the Institute of Emerging Diseases & Innovative Therapies in France and Harvard Medical School discovered that pioglitazone can work with the cancer drug imatinib so that it not only stops the spread of chronic myeloid leukemia but eliminates the cancer altogether. Cancer stem cells can “hide” from imatinib by becoming quiescent, but pioglitazone releases the cells from “hibernation” to allow the cancer drug to finish its job. The researchers are preparing for clinical trials on pioglitazone.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

