What molecules are we?

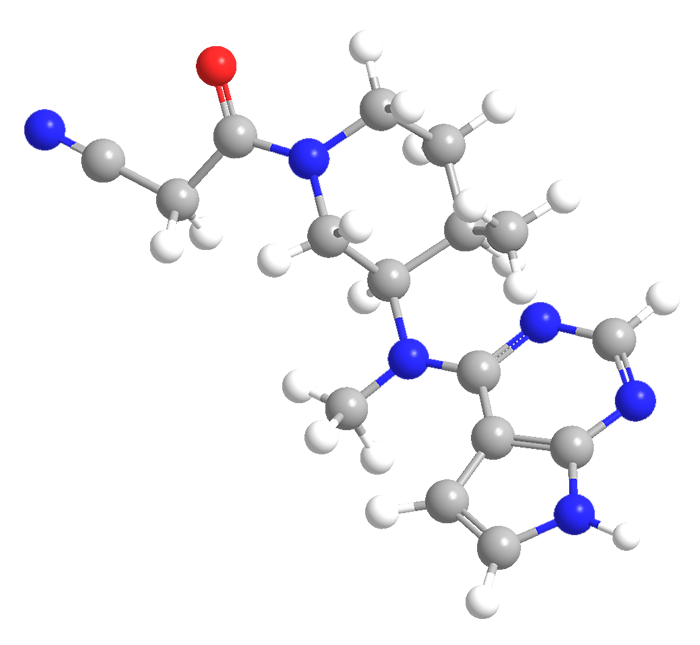

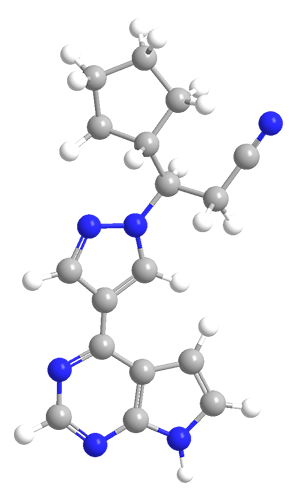
Tofacitinib (trade names Xeljanz and Jakvinus; Pfizer) and ruxolitinib (Jakafi and Jakavi; Incyte Pharmaceuticals and Novartis) are Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors that are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis and myelofibrosis, respectively. Tofacitinib (structure 1) was the first to be developed; it was the outgrowth of research performed at the National Institutes of Health by John O'Shea and co-workers.
Ruxolitinib (structure 2) did not come along until about 5 years ago. It may also be useful for treating other disease such as lymphoma, pancreatic cancer, and polycythemia vera.
Both drugs are now being looked at to treat a very widespread but much less serious condition: hair loss. A Columbia University team led by Angela M. Christiano observed that administering the drugs orally to mice promoted hair growth. The downside was that the animals' immune systems were compromised, so the researchers applied the drugs topically and obtained similar hair growth results.
It turns out that JAK inhibition is the key to this effect as it is for disease treatment. The drugs inhibit a kinase pathway in dormant hair follicle cells that causes the cells to transcribe DNA. Inhibiting the pathway "wakes up" the cells, and hair growth ensues.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

