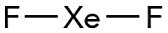
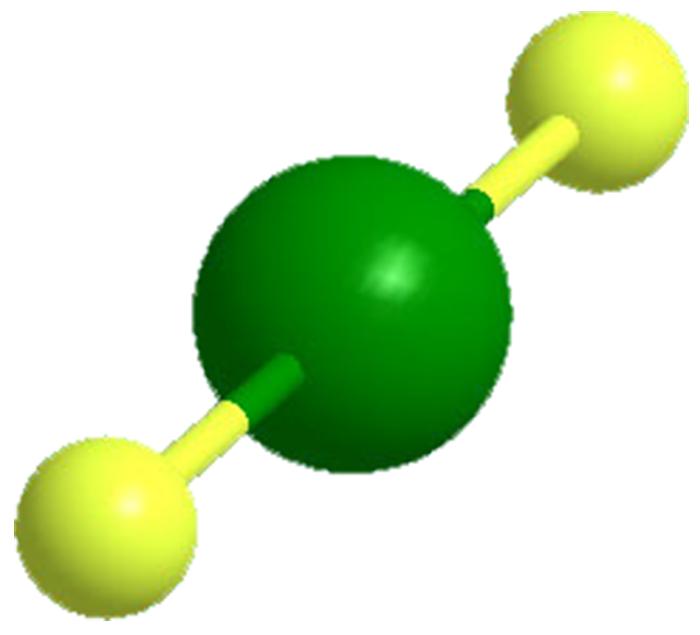
Xenon difluoride is a white crystalline solid with an unpleasant odor. One of the first compounds to be prepared from "inert" gases, it was synthesized by the low-pressure photochemical reaction of xenon and fluorine by J. L. Weeks, C. L. Chernick, and M. S. Matheson in 1962. The same year, R. Hoppe and co-workers produced it via electrical discharge. XeF2 is a strong fluorinating agent.
MOTW update:
June 19, 2023
Xenon difluoride1 (XeF2) is a white crystalline solid with an unpleasant odor, in 1962 it became one of the first compounds to be prepared from “inert” gases. Since then, it has been widely studied and incorporated into larger molecules. Earlier this month, Gary J. Schrobilgen and co-workers at McMaster University (Hamilton, ON) reported the synthesis of coordination complexes of XeF2 with the bromyl cation2 (BrO2+), such as [BrO2(XeF2)2][SbF6]. The authors described the properties of the complexes, including their coordination chemistry.
1. CAS Reg. No. 13709-36-9.
2. CAS Reg. No. 58409-45-3.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

