What molecule am I?

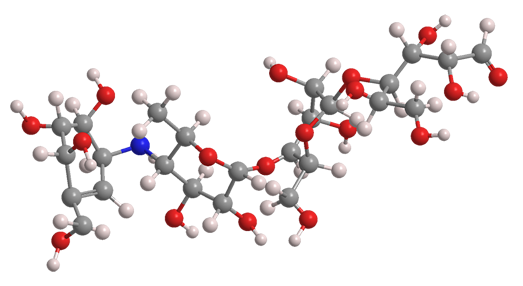
Acarbose is a modified tetrasaccharide that is used to treat type 2 diabetes and sometimes prediabetes. The images show the right-hand saccharide in its aldehyde form; but in solution, it cyclizes to form a pyranose.
Acarbose is an α-glucosidase inhibitor that prevents the enzymatic release of glucose from larger carbohydrates in the gut. This process aids in the treatment of diabetes by reducing the amount of sugar absorbed in the intestinal tract.
In the mid-1970s, six researchers at Bayer AG (Leverkusen, West Germany) were awarded German and US patents for the synthesis of acarbose and similar compounds. (The US patent is simply titled “Amino Sugar Derivatives”.) The description of the invention states that the compounds could be used to treat diabetes, adiposity, and hyperlipidemia; but no disease treatment is mentioned in the claims.
Acarbose, now a generic drug, is marketed under several tradenames worldwide. It is prescribed rarely in the United States, however, because it frequently causes diarrhea and flatulence. In contrast, it is very popular in China because it is inexpensive and the side effects are minimal. The difference is attributed to Chinese and other Asian diets, which contain considerably more carbohydrates than Western diets.
In May, chemist Daniel C. Whitehead, microbiologist Kristi Whitehead, and colleagues at Clemson University (SC) demonstrated that acarbose might be used to modify bacterial populations in the human microbiome. Specifically, in lab-grown cultures, the drug prevented the growth of Bacteroides species, which consume potato starch and the food additive fungal pullulan.
Although it is yet to be shown what effect acarbose has on the actual microbiome, Daniel Whitehead says, “This work is really a proof of concept that a small molecule can arrest the starch utilization system.”
Acarbose hazard information
| GHS classification*: not a hazardous substance |
*Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals.
Acarbose fast facts
| CAS Reg. No. | 56180-94-0 |
| Molar mass | 645.60 g/mol |
| Empirical formula | C25H43NO18 |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder |
| Melting point | 165–170 ºC (dec.) |
| Water solubility | 100–150 g/L |

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

