What molecule am I?
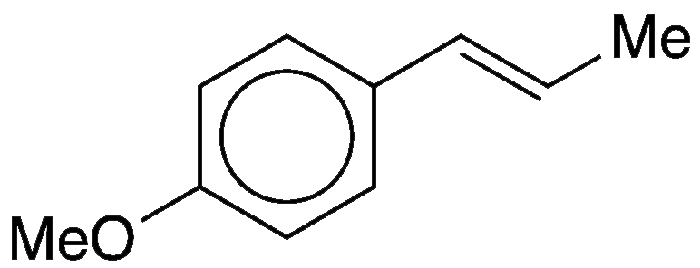
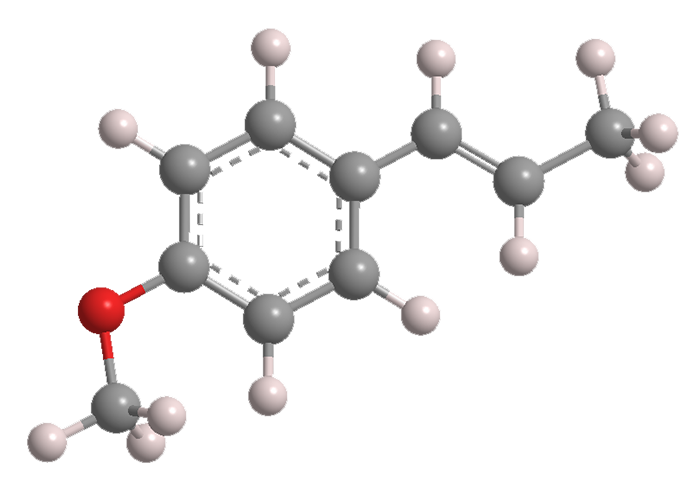
Anethole, formally 1-methoxy-4-[(1E)-prop-1-en-1-yl]benzene, is an anisole derivative that is the major constituent of the oils of anise (Pimpinella anisum), star anise (Illicium verum), and fennel (Foeniculum vulgare). Also known as “anise camphor”, it is used as a flavoring and aroma agent.
Fragrant oils have been extracted from anise and fennel plants since the Renaissance, but not until 1866 did German chemist Emil Erlenmeyer (of the eponymous flask) establish the structure of the primary substance derived from these oils. Most commercial anethole is currently derived from tree extracts such as turpentine. It is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for use in foods, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
Anethole is highly hydrophobic but soluble in ethanol, a combination that produces the “ouzo effect”. When ouzo and other anise-flavored liqueurs such as absinthe and arak are poured over ice or mixed with water, the mixtures spontaneously form highly stable emulsions. The ouzo effect is a potential mechanism for designing commercial surfactant-free emulsions without the need for expensive high-speed stabilization.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

