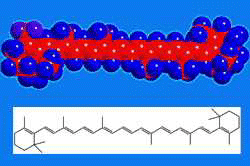
β-Carotene, one of several naturally occurring carotene isomers, is the most important of the A provitamins. It is widely distributed in the animal and plant kingdoms and is most abundant in yellow and orange fruits and vegetables such as mangoes, papayas, yams, and carrots. In biological systems, it is cleaved at the central C=C bond to form vitamin A by the enzyme β-carotene dioxygenase.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

