What molecule am I?

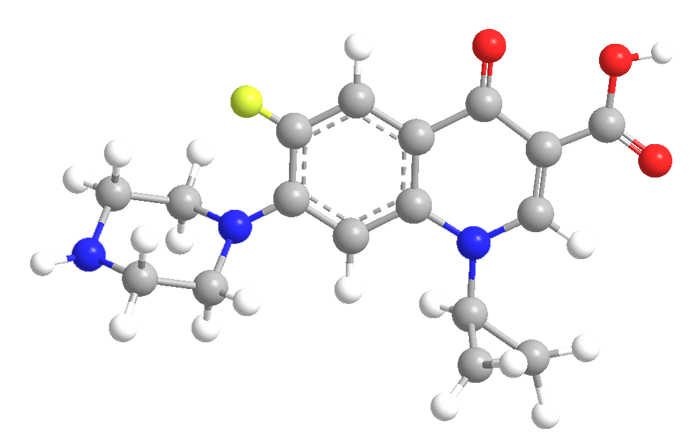
Ciprofloxacin, often called Cipro, its original trade name, is one of the world’s most widely prescribed antibiotics for bacterial infections. It is a member of the quinoline antibacterial class and is a descendant of norfloxacin, the first quinoline antibiotic to contain a fluorine atom.
In the 1980s, scientists at Bayer Pharmaceuticals discovered that replacing the ethyl group of norfloxacin with a cyclopropyl group greatly increased its Gram-negative bactericidal activity. In 1987, Bayer received US Food and Drug Administration approval for orally administered ciprofloxacin; the intravenous form was approved in 1991.
Since Bayer’s patent expired in 2004, ciprofloxacin has been widely distributed as an inexpensive broad-spectrum antibacterial. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

