What molecule am I?
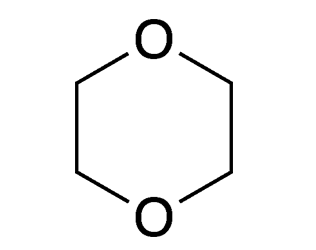
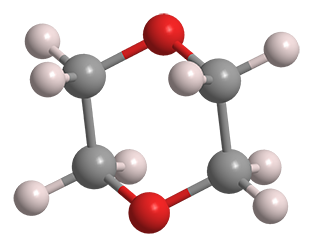
March of this year was “Solvent Month” for Molecule of the Week. Another commonly used solvent is 1,4-dioxane, usually referred to simply as dioxane.1 It is a cyclic diether that has an odor similar to that of its more volatile cousin, diethyl ether.
In 1928, IG Farbenindustrie (precursor to BASF) patented a manufacturing process for dioxane in which diethylene glycol is heated with a small amount of sulfuric acid. Today, it is still produced in much the same way. It is used industrially as a solvent for cellulose esters and ethers, adhesives, inks, and many other materials.
Dioxane, however, is coming under regulatory pressure because of health and environmental concerns:
- A suspected carcinogen, dioxane has been found to contaminate drinking water in 27 US states.
- Significant amounts of the solvent have been found in groundwater in New York State, prompting a bill in the legislature that would ban it in cleaning and personal care products.
- The US Occupational Safety and Health Administration is considering regulating worker exposure to dioxane.
1. Structural isomers 1,2- and 1,3-dioxane have been prepared, but they are not commercial products.
1,4-Dioxane hazard information
| GHS classification*: flammable liquids, category 2 | |
| H225—Highly flammable liquid and vapor | |
| GHS classification: serious eye damage/eye irritation, category 2A | |
| H319—Causes serious eye irritation | |
| GHS classification: specific target organ toxicity, single exposure, respiratory tract irritation, category 3 | |
| H335—May cause respiratory irritation | |
| GHS classification: carcenogenicity, category 2 | |
| H351—Suspected of causing cancer | |
*Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals. Explanation of pictograms.
MOTW update: November 18, 2019
Former Molecules of the Week 1,4-dioxane, hexabromocyclododecane, 1-bromopropane, N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, and dichloromethane, among several other chemicals, are at the center of a controversy about how the EPA’s scientific advisory committees are evaluating risks of air pollution. The problems are the lack of expertise in some of the committees and a shortage of adquate data to evaluate the chemicals. Industrial and environmental stakeholders are critical of the latest risk assessments.
1,4-Dioxane fast facts
| CAS Reg. No. | 123-91-1 |
| Empirical formula | C4H8O2 |
| Molar mass | 88.11 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Melting point | 11.8 ºC |
| Boiling point | 101.1 ºC |
| Water solubility | Miscible |
MOTW update:
January 18, 2021
Dioxane is a valuable solvent that has many industrial and laboratory uses. In 2019, it came under regulatory pressure because it is a possible carcinogen and has been found in drinking water and groundwater in several states. On December 31, 2020, the US Environmental Protection Agency released a hastily compiled risk assessment of dioxane that pleased neither environmentalists, state attorneys general, nor the chemical industry. Among the report’s other shortcomings, EPA ignored drinking-water exposure; environmentalists and regulators say that this is dioxane’s greatest threat to the general population.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

