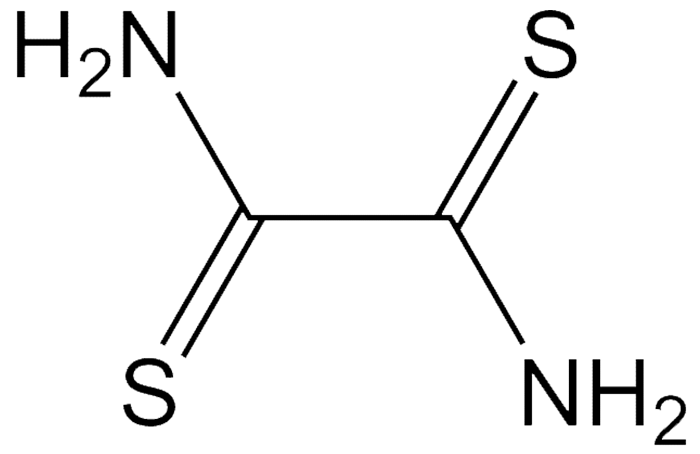
Dithiooxamide, originally known as rubeanic acid, is a deep red crystalline solid with a decomposition temperature of ≈200 ºC. It is a chelating agent for the detecting determining copper, cobalt, and nickel. It is also used to stabilize ascorbic acid in acidic solutions.
In early 2015, H. Firouzabadi, N. Iranpoor, and co-workers at Shiraz University (Iran) discovered that dithiooxamide can be used as a thiolating agent. Because it is stable, odorless, and commercially available, it is an excellent alternative to thiol reagents, which are foul-smelling and often require harsh reaction conditions. It reacts with alkyl or benzyl halides in base at 35 ºC to form sulfides. With aryl halides, the reaction is run at 120 ºC with a catalyst

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

