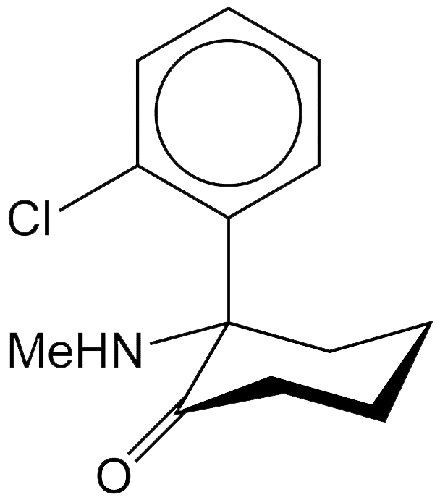
Ketamine is a drug that has long been used as an anesthetic, sedative, analgesic, and antidepressant. It was developed in the mid-1960s by researchers at Parke-Davis (now a Pfizer subsidiary). One of its first uses was for American servicemen during the Vietnam War.
Anesthetics are used in a multitude of medical procedures, but little is known about their mode of action in the nervous system. R. G. Eckenhoff and co-workers at the University of Pennsylvania recently discovered that ketamine binds to and activates olfactory receptors in mouse brains. They believe that these receptors may be prime targets for new anesthetics.
MOTW Update: May 1, 2017
Recently, the journal ACS Chemical Neuroscience published an extensive review of ketamine’s importance in neurochemistry.
MOTW update:
April 22, 2019
Ketamine is a versatile 1960s-era drug that over the years has been used as an anesthetic and antidepressant. As effective as it is, scientists have been unable to determine its mode of action. But this month, Conor Liston and colleagues at Weill Cornell Medicine (New York City) reported that when they injected ketamine into “depressed” mice, the animals began to regrow dendritic spines on their nerve cells and came out of their lethargy.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

