What molecule am I?
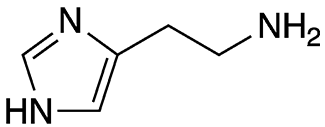
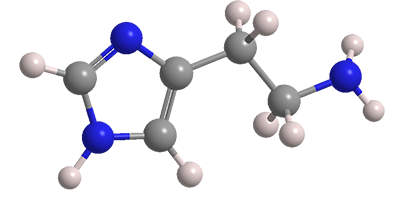
Histamine is an organic triamine that is a strong vasodilator found in blood and most bodily tissues. It is involved in inflammatory and immune responses. Histamine is stored primarily in mast cells and basophils; it is released in response to tissue damage caused by injury, infection, or allergens.
In 1938, French microbiologists Lévy-Brühl and Ungar showed that pneumococcus bacteria and Balantidium coli biosynthesize histamine from the amino acid histidine. It was later shown that this reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme histidine decarboxylase.
Histamine has many physiological functions, but this time of year we focus on its role in reactions to allergens such as pollen. Allergens bind to the antibody immunoglobulin E in the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity, releasing histamine, and leading to runny noses, watery eyes, sneezing, and nasal congestion. Fortunately, many antihistamines are available to combat these symptoms.
Histamine hazard information
| GHS classification*: acute toxicity, oral, category 3 | |
| H301—Toxic if swallowed | |
| GHS classification: skin irritation, category 2 | |
| H315—Causes skin irritation | |
| GHS classification: skin sensitization, category 1 | |
| H317—May cause an allergic skin reaction | |
| GHS classification: eye irritation, category 2A | |
| H319—Causes serious eye irritation | |
| GHS classification: respiratory sensitisation, category 1 | |
H334—May cause allergy or asthma symptoms or breathing difficulties if inhaled | |
| GHS classification: specific target organ toxicity, single exposure, category3 | |
| H335—May cause respiratory irritation | |
*Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals. Explanation of pictograms.
Histamine fast facts
| CAS Reg. No. | 51-45-6 |
| Molar mass | 111.15 g/mol |
| Empirical formula | C5H9N3 |
| Appearance | White crystals or powder |
| Melting point | 83–84 ºC |
| Water solubility | 34 g/L |

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

