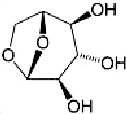
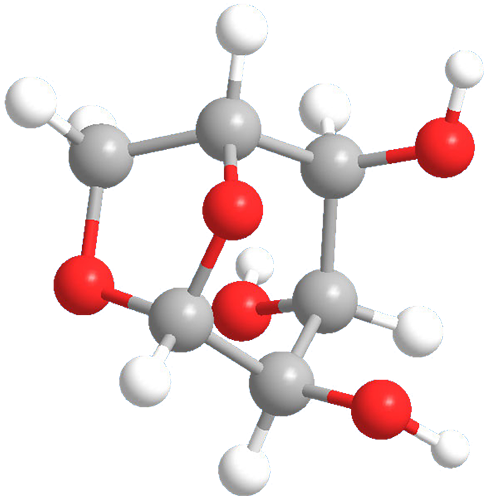
Levoglucosan, a substance formed by heating carbohydrates, has an unusual heterocyclic bicyclo[3.2.1]octane structure. In 1970, C. M. Lakshmann and H. E. Hoelscher reported that it can be produced in large quantities by pyrolyzing cornstarch under the proper conditions. Levoglucosan is often used as a marker for detecting biomass burning in air quality studies. It is also an initial product of wood decomposition during forest fires.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

