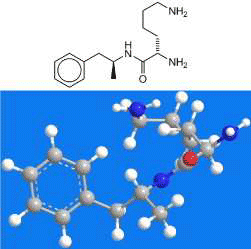
Lisdexamfetamine—trade name Vyvanse—is amphetamine coupled with l-lysine. It is being developed to treat attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in pediatric patients. It provides controlled release of amphetamine via hydrolysis within the body and decreases the potential for abuse because crushing the capsule does not accelerate its activation.
MOTW update: June 3, 2024
Lisdexamfetamine1 is a prodrug for treating attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) that was approved by FDA in 2007. Under the trade name Vyvanse, it is an alternative to the more commonly used drug Adderall.
Whereas Adderall is a combination of salts of racemic amphetamine2 and its enantiomer D-amphetamine3, lisdexamfetamine is a single molecule consisting of dextroamphetamine coupled with L-lysine4. In a 2022 article, Richard Crabbe at Free by the Sea drug and alcohol recovery center (Ocean Park, WA) explained the differences between Adderall and Vyvanse5.
Among the differences is that Vyvanse is significantly slower to be absorbed by the body than Adderall because it must first release D-amphetamine. Vyvanse’s slower absorption rate, however, leads to fewer side effects than Adderall.
In 2015, FDA approved Vyvanse for treating binge eating disorder. Last August, FDA approved generic lisdexamfetamine as an alternative to brand-name Vyvanse.
1. CAS Reg. No. 608137-32-2.
2. CAS Reg. No. 300-62-9.
3. CAS Reg. No. 51-64-9.
4. CAS Reg. No. 56-87-1.
5. Our thanks to a reader who sent this article to MOTW.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

