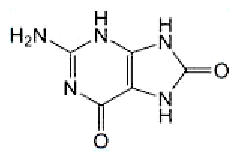
8-Oxoguanine, also known as its tautomer 8-hydroxyguanine, is a common DNA lesion that results from exposure to reactive oxygen species. In 2007, J. J. Collins and co-workers at Boston University showed that antibiotics with diverse targets kill bacterial cells by generating hydroxyl radicals. More recently, Collins’s group and G. C. Walker and colleagues at MIT reported that guanine oxidation to 8-oxoguanine is bacterial antibiotics’ main mechanism for killing cells.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

