What molecule am I?

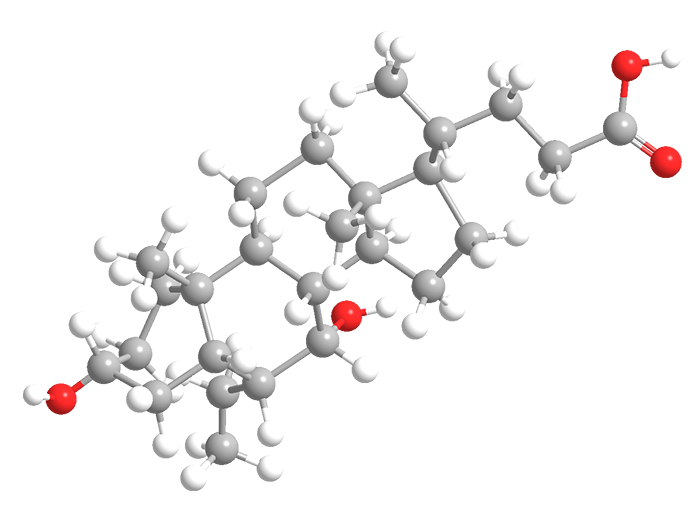
Obeticholic acid (OCA) is a semisynthetic bile acid that is analogous to the natural acid chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA). One of the two primary bile acids produced in the human liver, CDCA is the most active physiological ligand for the farnesoid X receptor (FXR).
FXR has several biochemical functions in the liver and intestine. In response to the rise of the virulent liver disease nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), researchers have identified FXR as the one of the key targets for treating it. Multiple FXR agonists are being tested to treat NASH; OCA, a product of Intercept Pharmaceuticals (New York), is the front-runner as the result of a 2014 Phase 2 study. A Phase 3 study is under way.
OCA has two notable side effects: itchiness and an increase in LDL (“good” cholesterol). Although both can be controlled by additional drugs, Intercept’s competitors believe that synthetic FXR agonists could be more effective and have fewer negative side effects than OCA.
For a broader discussion of NASH, see Lisa M. Jarvis’s cover story in this week’s C&EN.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

