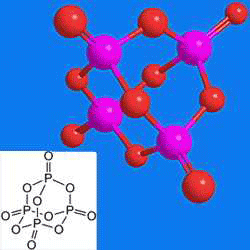
Phosphorus pentoxide (empirical formula P2O5) is known to many laboratory workers as a powerful desiccant. It is manufactured by burning elemental phosphorus in a current of dry air. P2O5 exists in several crystalline and amorphous forms, the most common of which is the crystalline P4O10 shown. In the fertilizer industry, phosphorus concentration is expressed as weight percent P2O5 equivalent.
MOTW update:
February 28, 2022
Phosphorus pentoxide1 (P4O10) is a powerful drying agent that can also be used to remove the elements of water from organic and inorganic compounds.
P4O10 has also found use as a metal-free acid catalyst. In a recent example, Evgeny A. Mostovich and colleagues at Novosibirsk State University (Russia) used it to promote the cyclization of di[aryl(heteroaryl)methyl]malonic acids en route to fused, π-extended spiro[4.4]nonane-1,6-diones, which may have valuable optoelectronic applications.
1. CAS Reg. No. 16752-60-6.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

