What molecules are we?
Robert Burns Woodward is generally considered to be the greatest synthetic organic chemist of the 20th century. From the 1940s to the 1970s, he led the syntheses of numerous natural products and pharmaceuticals. In 1965, Woodward received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this body of work.
Over the years, Molecule of the Week has featured several “Woodward molecules”, including quinine, cholesterol, cortisone, strychnine, and chlorophyll. Here are four more of those important compounds with the dates their syntheses were reported.
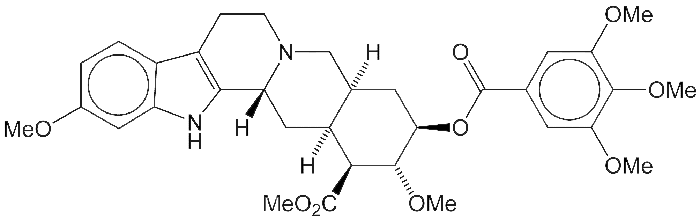
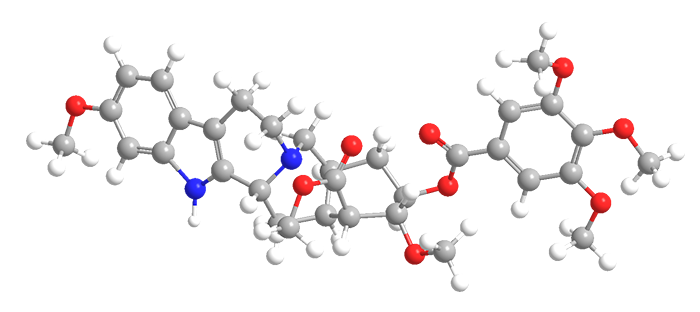
Reserpine (1958) was originally isolated from Rauwolfia serpentina in 1952. It was once used as a treatment for high blood pressure and psychotic episodes, but it has been replaced by newer drugs with fewer side effects.
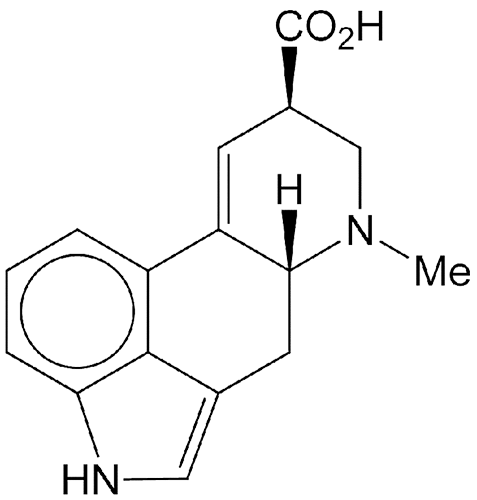
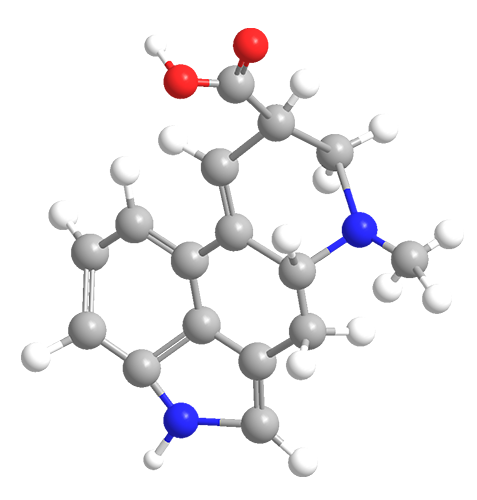
Lysergic acid (1956) is the biosynthetic precursor for several ergoline alkaloids. Its most notorious end product is LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide), a psychedelic drug promoted by Timothy Leary in the 1960s.
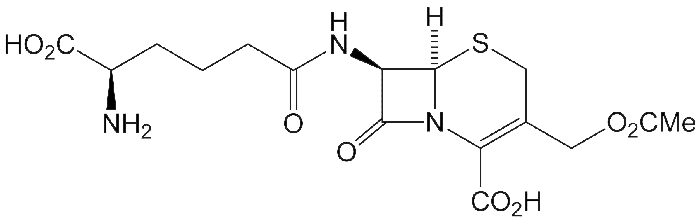
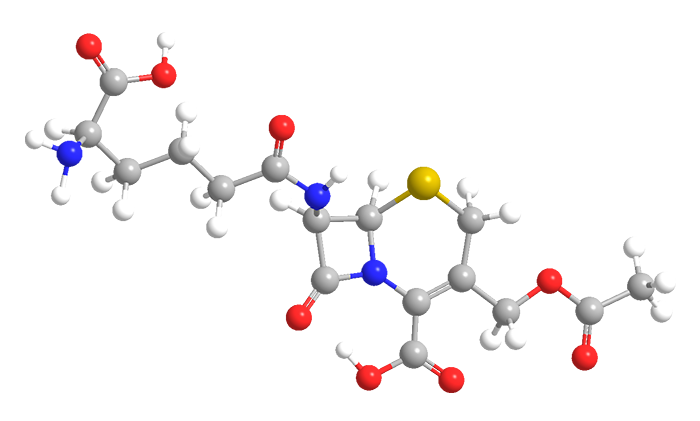
Cephalosporin C (1966) is a member of the cephalosporin family of β-lactam antibiotics. They were discovered in 1945 in Acremonium fungus species.
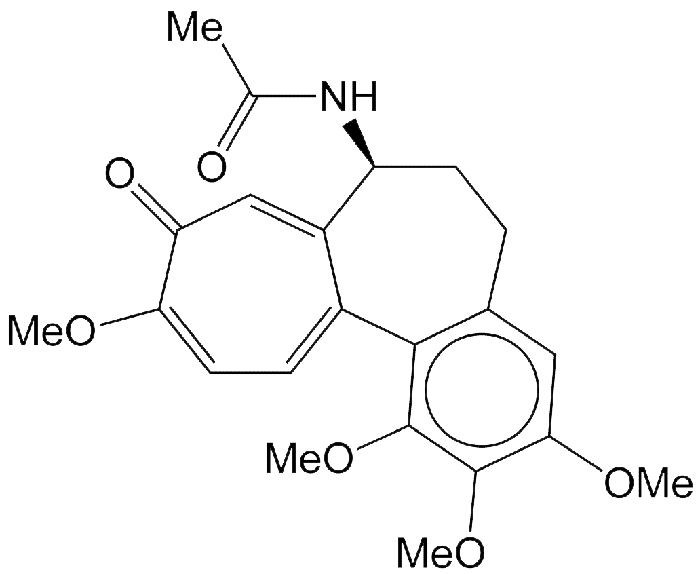
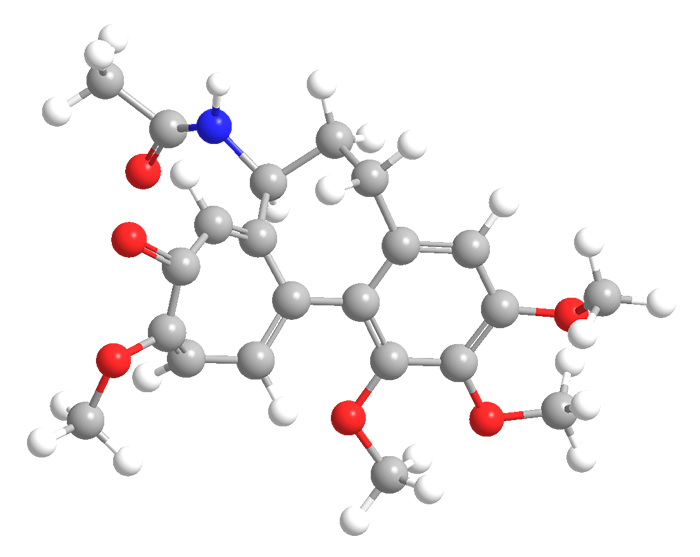
Colchicine (1963), primarily used to treat gout, dates to prehistoric times when its source, the Colchicum autumnale (crocus) plant, was used to treat rheumatism and swelling.
Woodward’s crowning synthetic accomplishment was vitamin B12 (cobalamin) in 1972. For this work, he collaborated with Swiss chemist Albert Eschenmoser and more than 100 graduate students and postdoctoral fellows. Each of the research groups contributed a portion of the molecule.
Woodward’s achievements in physical organic chemistry were also ground-breaking. Using molecular orbital theory, he and theoretical chemist Roald Hoffmann formulated rules that govern pericyclic reactions, such as cycloadditions. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in chemistry for the Woodward–Hoffman rules, 2 years after Woodward’s death.
Bethany Halford’s article in this week’s issue of C&EN commemorates Woodward’s career.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

