What molecule am I?
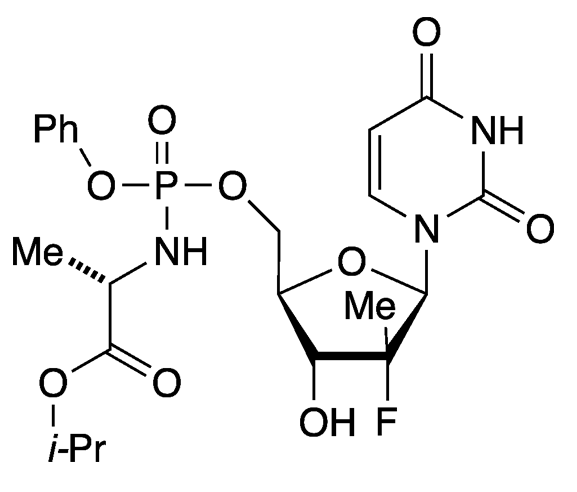

Hepatitis C is a burgeoning disease that is still in search of a one-drug-fits-all solution. Currently, each hepatitis C virus genotype is treated with a pharmaceutical cocktail that consists of a mixture of antivirals, most of whose names end with “vir”.
Sofosbuvir is one such compound. It was discovered in 2007 by Michael Sofia at Pharmasset (now part of Gilead Sciences) and approved for use in the United States by the Food and Drug Administration in 2013. The FDA approval was for the combination of sofosbuvir and ribavirin, an antiviral that dates back to 1972. Sofosbuvir is the active ingredient in Gilead’s products Sovaldi and Harvoni, ads for which you may have seen on TV.
Sofosbuvir was the subject of a high-profile patent lawsuit involving Gilead and drug giant Merck. Merck contended that sofosbuvir was patterned after a patent awarded to Idenix Pharmaceuticals, a company that Merck had acquired. After a series of trials, a federal jury ordered Gilead to pay Merck US$2.54 billion (that’s right, billion) for infringing the Idenix patent.
Gilead appealed; and this past February, the judge in a US district court overturned the award, writing that the Idenix patent was too broad and that a skilled chemist could not easily derive sofosbuvir from the information in the patent. For the same reason, the judge invalidated the patent.
Merck has vowed to appeal the overturn ruling.
Sofosbuvir hazard information
| GHS classification*: skin irritation, category 2 | |
| H315—Causes skin irritation | |
| GHS classification: skin sensitization, category 1 | |
| H317—May cause an allergic skin reaction | |
| GHS classification: serious eye damage, category 1 | |
| H318—Causes serious eye damage | |
| GHS classification: respiratory sensitisation, category 1 | |
| H334—May cause allergy or asthma symptoms or breathing difficulties if inhaled | |
| GHS classification: specific target organ toxicity, single exposure, respiratory tract irritation, category3 | |
| H335—May cause respiratory irritation | |
| GHS classification: germ cell mutagenicity, category 2 | |
| H341—Suspected of causing genetic defects | |
| GHS classification: reproductive toxicity, category 2 | |
| H361—Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child | |
| GHS classification: specific target organ toxicity, single exposure, category 1 | |
| H370—Causes damage to organs | |
| GHS classification: hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard, category 4 | |
| H413—May cause long-lasting harmful effects to aquatic life | |
*Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals. Explanation of pictograms.
Sofosbuvir fast facts
| CAS Reg. No. | 1190307-88-0 |
| Molar mass | 529.46 g/mol |
| Empirical formula | C22H29FN3O9P |
| Appearance | White to off-white crystals or powder |
| Melting point | 94–125 ºC* |
| Water solubility | ≈105 mg/L* |
*Depends on crystalline polymorph.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

