What molecule am I?

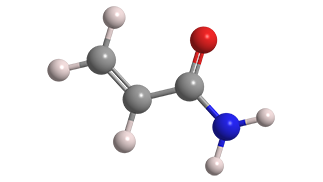
Acrylamide is the simplest unsaturated organic amide. Despite its low molar mass, and because it is highly polar, it is a solid rather than a liquid. As the hazard information table indicates, it is extremely toxic in multiple ways.
In 1949, Otto Bayer at Bayer AG (Leverkusen, West Germany) described the preparation of acrylamide. (Bayer was not related to the founding Bayer family.) Chemist Bayer synthesized acrylamide via the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of acrylonitrile. This is the only manufacturing method in use today. But in 2019, Kemira Ltd. (Helsinki, Finland) announced that it will begin to produce biobased acrylamide in its Mobile, AL, plant.
By far the major use of acrylamide is polymerization into polyacrylamides, which, depending on their molar masses and degree of cross-linking, are valuable for flocculating solids suspended in water, thickening water for use in enhanced petroleum recovery, and agricultural soil conditioning.
Acrylamide has become notorious in the past 20 years because traces of it have been found in commercial and home-cooked foods. Most of these are starchy foods such as French fries, potato chips, and some breads. In general, higher temperatures and longer cooking times increase the formation of acrylamide. Smoking tobacco, however, results in much higher blood acrylamide concentrations than any food source.
Acrylamide hazard information
| GHS classification*: acute toxicity, oral, category 3 | |
| H301—Toxic if swallowed | |
| GHS classification: acute toxicity, dermal, category 4 | |
| H312—Harmful in contact with skin | |
| GHS classification: skin corrosion/irritation, category 2 | |
| H315—Causes skin irritation | |
| GHS classification: skin sensitization, category 1 | |
| H317—May cause an allergic skin reaction | |
| GHS classification: serious eye damage/eye irritation, category 2A | |
| H319—Causes serious eye irritation | |
| GHS classification: acute toxicity, inhalation, category 4 | |
| H332—Harmful if inhaled | |
| GHS classification: germ cell mutagenicity, category 1B | |
| H340—May cause genetic defects | |
| GHS classification: carcinogenicity, category 1B | |
| H350—May cause cancer | |
| GHS classification: reproductive toxicity, category 2 | |
| H361f—Suspected of damaging fertility | |
| GHS classification: specific target organ toxicity, oral, repeated exposure, category 1 | |
| H372—Causes damage to organs (testes, peripheral nervous system) through prolonged or repeated exposure if swallowed | |
**Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals. Explanation of pictograms.
Acrylamide fast facts
| CAS Reg. No. | 79-06-1 |
| SciFinder nomenclature | 2-Propenamide |
| Empirical formula | C3H5NO |
| Molar mass | 71.08 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Melting point | 84.5 ºC |
| Water solubility | 2.04 kg/L (25 ºC) |

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

