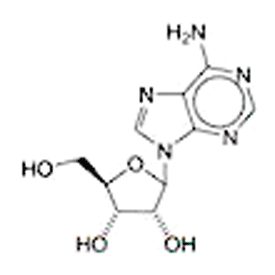
Adenosine is a nucleoside found widely in nature, and it is one of the components of the important energy-transfer coenzymes adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and diphosphate (ADP). It was first isolated from yeast nucleic acid; several researchers reported its structure in the 1930s. More recently, M. Nedergaard and co-workers showed that adenosine released during acupuncture acts as a painkiller.
MOTW update: June 26, 2023
Adenosine and inosine were the Molecules of the Week for June 5, 2010, and July 15, 2019, respectively. They are nucleosides that differ only by the hydroxyl configurations on the ribofuranose ring. In 2019, researchers found that a gene editor unexpectedly converted a small amount of adenosine in an RNA to inosine.
Earlier this month, Eli Eisenberg and collaborators at Tel Aviv University, the University of Connecticut Health Center (Farmington), Bar-Ilan University (Ramat Gan, Israel), and the University of Puerto Rico (San Juan) reported that this conversion can be advantageous to squids and other cephalopods. The researchers found that seawater temperature decreases induce the cephalopods to self-edit mRNA adenosine to inosine. The nucleoside transformation enables the animals to prevent low-temperature “brain freeze”.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

