What molecule am I?

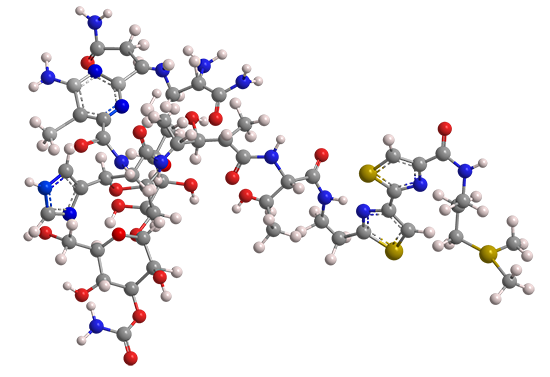
The term “bleomycin” represents a group of glycopeptides used as cancer drugs and antibiotics. It was discovered in 1962 by microbiologist Hamao Umezawa at the Institute of Microbial Chemistry (Tokyo), who observed that culture filtrates of the bacterium Streptomyces verticillus had anticancer activity.
All bleomycins have the same general structure; they differ only by the functional group attached to the terminal amine. The most prominent member, bleomycin A2 (shown), contains a (dimethylsulfonio)propyl cation on the amine. It is marketed in the form of a sulfate salt that contains other bleomycins. The total synthesis of bleomycin A2 was reported in 1981 by Umezawa and colleagues at several Japanese research institutions. The commercial product, however, is obtained from S. verticillus.
Bleomycin sulfate is used primarily to treat Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma; testicular and cervical cancers; squamous cell carcinomas; and cancer-related pleural effusion. It is administered via intravenous and intramuscular injection.
Biochemist JoAnne Stubbe at MIT (Cambridge, MA) was awarded the 2020 Priestley Medal for her work on enzyme mechanisms and for uncovering the details of the mechanism of action of bleomycin, which cleaves double-stranded DNA. Stephen J. Lippard, also at MIT, calls Stubbe “the top mechanistic biochemist of her generation”. The Priestley Medal for lifetime achievement in chemistry is the highest award given by ACS.
Bleomycin hazard information
| Hazard class* | Hazard statement | |
|---|---|---|
| Germ cell mutagenicity, category 1B | H340—May cause genetic defects | |
| Carcinogenicity, category 2 | H351—Suspected of causing cancer | |
| Reproductive toxicity, category 2 | H361—Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child | |
*Data for mixed bleomycin sulfate.
**Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals. Explanation of pictograms.
Bleomycin fast facts
| CAS Reg. No. | 11116-31-7 |
| SciFinder nomenclature | Bleomycinamide, N1-[3-(dimethylsulfonio)-propyl]- |
| Empirical formula | C55H84N17O21S3+ |
| Molar mass | 1415.55 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to yellowish powdera |
| Melting point | 200–204 ºC (dec.)a |
| Water solubility | 20 g/La |
a. Data for mixed bleomycin sulfate, CAS Reg. No. 9041-93-4.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

