What molecule am I?

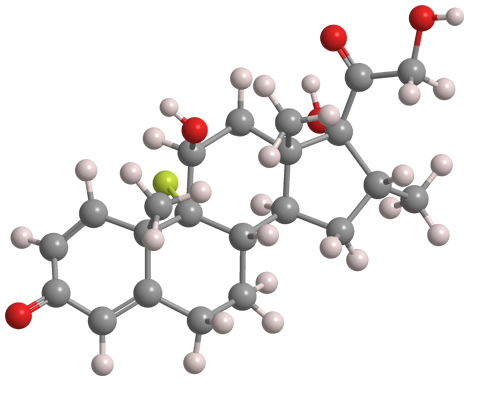
Dexamethasone is a venerable corticosteroid medication that has been used against a wide range of diseases and conditions. Wikipedia credits the first preparation of the drug in 1957 to physician Philip S. Hench and co-workers at the Mayo Clinic (Rochester, MN); but no peer-reviewed references are cited. (Hench was a co-winner of the 1950 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine for the discovery of cortisone.)
The following year, Glen E. Arth and colleagues at Merck (Rahway, NJ) reported the synthesis of dexamethasone as part of their search for new steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines. One month later, Eugene P. Oliveto and coauthors at Schering (Bloomfield, NJ) and Massachusetts General Hospital (Boston) published a different synthesis. Patents describing dexamethasone syntheses were awarded to two other drug companies in 1961.
Dexamethasone has been used to treat allergies, brain swelling, tuberculosis, autoimmune conditions, and several lung diseases. Its versatility prompted the World Health Organization to include it in its Model List of Essential Medicines. But dexamethasone has many adverse side effects that range from acne to vertigo.
Perhaps it is not surprising that the variety of dexamethasone’s medical uses has led researchers to administer it to COVID-19 patients. In a British study called RECOVERY (for Randomised Evaluation of COVID-19 Therapy), more than 11,000 patients with serious cases of the disease were given one of several treatments, including oral or injected dexamethasone. Of the approximately 2100 subjects given dexamethasone, the patients on ventilators had one-third fewer deaths compared with control subjects. Those who required oxygen without a ventilator had about 20% fewer deaths.
It should be noted that as of June 22, 2020, the study’s results had not been peer-reviewed.
Dexamethasone hazard information
| Hazard class* | Hazard statement** | |
|---|---|---|
| Reproductive toxicity, category 1B | H360Df—May damage the unborn child; suspected of damaging fertility | |
*Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals.
Explanation of pictograms.
**Some safety data sheets cite as many as six additional hazard statements.
Dexamethasone fast facts
| CAS Reg. No. | 50-02-2 |
| SciFinder nomenclature | Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 9-fluoro-11,17,21-trihydroxy-16-methyl-, (11β,16α)- |
| Empirical formula | C22H29FO5 |
| Molar mass | 392.46 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| Melting point | 262–264 ºC |
| Water solubility | 89 mg/L |
MOTW Update
1-Bromopropane was the Molecule of the Week for September 30, 2019. The hazards associated with this valuable industrial solvent and degreasing agent were reviewed in 2019 by the US Environmental Protection Agency. The agency reported that it could pose “unreasonable risks to workers, occupational nonusers, consumers, and bystanders under certain conditions of use.” In June 2020, EPA added 1-bromopropane to its list of hazardous air pollutants under the Clean Air Act—the first chemical added since the act was amended in 1990.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

