What molecule am I?
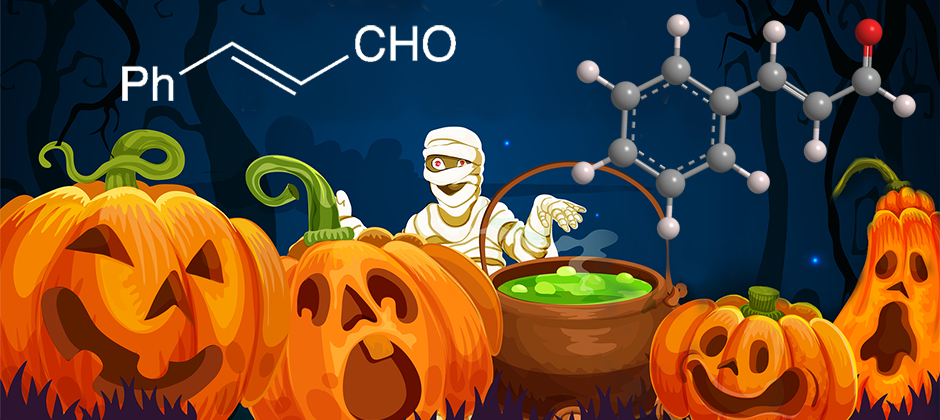
trans-Cinnamaldehyde, as its name suggests, is a natural product that occurs in cinnamon oils. Its cis counterpart is not found in nature; thus, “trans” is often omitted from its name.
As early as the 1830s, chemists reported synthesizing cinnamaldehyde via the aldol condensation of benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde. But the most economical way of producing it is still by steam distilling the bark of trees in the genus Cinnamomum.
Cinnamaldehyde is an important flavoring in foods (e.g., candy and cookies) and an odorant for perfumes. It has also been used to eradicate mosquito larvae and repel adult mosquitoes. Because it exists naturally, it is suitable for organic agriculture.
Now for a different take on cinnamaldehyde. Halloween is almost here, with its ghosts, witches, hobgoblins—and mummies. It turns out that the ancient Egyptians (ca. 2600 BCE) used the bark of cassia trees (Cinnamomum cassia) as an insecticide to help preserve mummies and give them a pleasing aroma.
Happy Halloween to you and your mummy!
trans-Cinnamaldehyde hazard information
| GHS classification*: flammable liquids, category 4 | |
| H227—Combustible liquid | |
| GHS classification: skin corrosion/irritation, category 2 | |
| H315—Causes skin irritation | |
| GHS classification: skin sensitization, category 1 | |
| H317—May cause an allergic skin reaction** | |
| GHS classification: serious eye damage/eye irritation, category 2A | |
| H319—Causes serious eye irritation** | |
| GHS classification: specific target organ toxicity, single exposure; respiratory tract irritation, category 3 | |
| H335—May cause respiratory irritation | |
*Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals. Explanation of pictograms.
trans-Cinnamaldehyde
fast facts
| CAS Reg. No. | 14371-10-9 |
| Empirical formula | C9H8O |
| Molar mass | 132.16 g/mol |
| Appearance | Yellow oily liquid |
| Boiling point | 250–253 ºC |
| Water solubility | ≈1.4 g/L |
MOTW update:
November 27, 2023
trans-Cinnamaldehyde1 was the Molecule of the Week for October 28, 2019. A constituent of cinnamon oils, it is an important food flavoring and perfume odorant. Earlier this month, Chen Jin, Zong-yi Wu, Lei Yang, and co-workers at Wenzhou Medical University (China) and Key Laboratory of Orthopedics of Zhejiang Province (Wenzhou) reported that trans-cinnamaldehyde has a beneficial health effect. They found that the compound alleviates bone loss by targeting oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage via the nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2/HO-1 signaling pathway in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and ovariectomized mice.
1. CAS Reg. No. 14371-10-9.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

