What molecule am I?
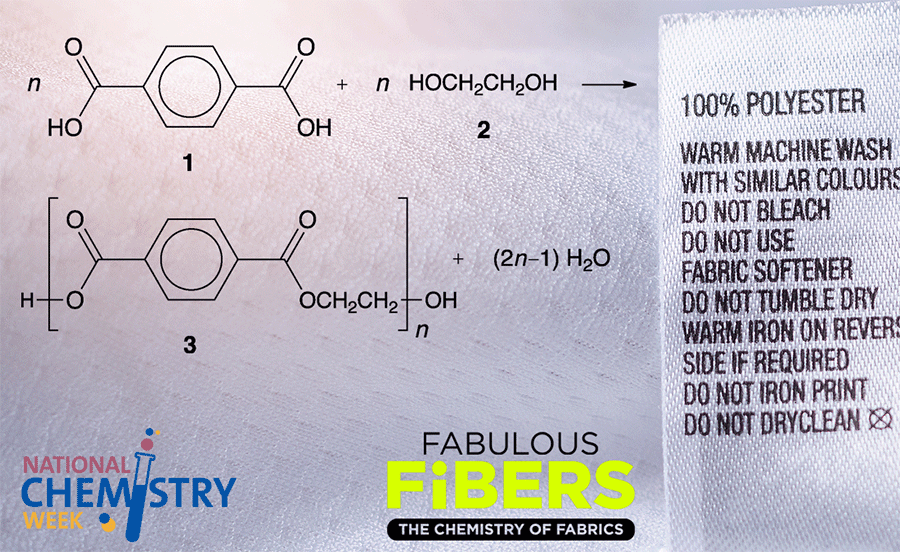
Poly(ethylene terephthalate), known familiarly as PET, is a condensation copolymer of ethylene glycol1 and terephthalic acid2. It is often incorrectly expressed as polyethylene terephthalate, without the parentheses.
As shown in the chemical equation, PET is made industrially by the reaction of equimolar amounts of terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol at 220–260 °C and 0.3–0.6 MPa pressure. Another commercial process begins with dimethyl terephthalate3 instead of the free acid and proceeds under similar conditions. Annual worldwide production exceeds 30 million tonnes.
Although most of us are familiar with so-called “PET bottles” for water and soft drinks, bottles consume only ≈30% of PET production. About 60% of PET is spun into fibers that are used in fabrics for fashion apparel, thermal wear, sportswear, workwear, and upholstery. In the fiber and fabric industries, PET is commonly called “polyester”.
In 2021, Peter Dubruel, Sandra Van Vliergerghe, and colleagues at Ghent University (Belgium) published an excellent review of the chemistry and applications of poly(ethylene terephthalate) and other commercial poly(alkylene terephthalate)s.
PET, or polyester, is currently being celebrated as a “fabulous fiber” during National Chemistry Week!
1. CAS Reg. No. 107-21-1.
2. CAS Reg. No. 100-21-0.
3. CAS Reg. No. 120-61-6.
Poly(ethylene terephthalate) hazard information
| Hazard class* | GHS code and hazard statement |
|---|---|
| Not a hazardous substance or mixture |
*Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals.
MOTW update
Ketene1 was the Molecule of the Week for June 27, 2016. It is a colorless, toxic gas that is useful in organic synthesis. This month, Guangjin Hou, Xiulian Pan, Xinhe Bao, and co-workers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Dalian) described the chemistry of converting ketene to gasoline-range hydrocarbons by passing it over H-SAPO-11 molecular sieves2 at temperatures up to 400 °C.
1. CAS Reg. No. 463-51-4.
2. H-SAPO-11 is an acidified medium-pore silicoaluminophosphate molecular sieve, CAS Reg. No. 308075-33-4.
Poly(ethylene terephthalate)
fast facts
| CAS Reg. No. | 25038-59-9 |
| SciFinder nomenclature | Poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyloxycarbonyl-1,4-phenylenecarbonyl) |
| Empirical formula | (C10H8O4)n |
| Molar mass | Variable; 10–50 kg/mol |
| Appearance | Transparent amorphous or semicrystalline solid |
| Melting point | Variable; generally 250–260 °C |
| Water solubility | Insoluble |

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

