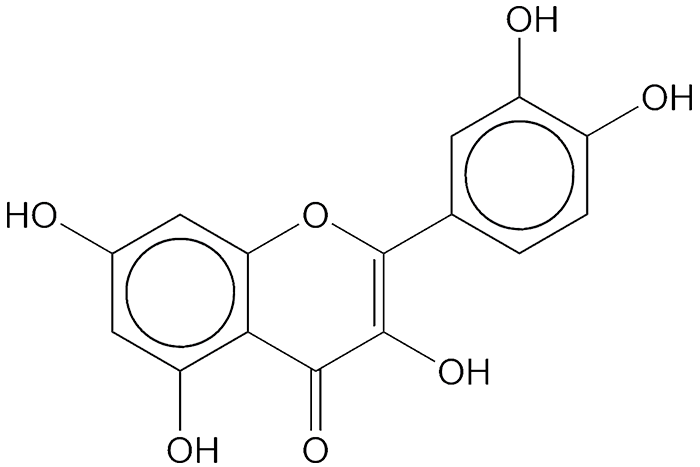
Quercetin is a flavonoid that occurs in many plant parts including rinds, barks, clover blossoms, and ragweed pollen. Capers are an especially rich source of quercetin. In 1962, S. Rangaswami and co-workers isolated it from Rhododendron cinnabarinum, a shrub that grows at high altitudes in Southeast Asia.
Quercetin’s bioavailability is poor, but its glycosides are readily absorbed by the body. It has been used to treat conditions ranging from eczema and inflammation to cancer and asthma. No clinical trials, however, have convincingly demonstrated its value; and it has not been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for any use.
MOTW update: May 22, 2023
Quercetin is a plant flavonoid that is used as a supplement to treat various health conditions. The US Food and Drug Administration designates it as “generally recognized as safe” but has not approved it for any medical use. In a report earlier this month, Xingtao Zhou, Shaoping Nie, and co-workers at Nanchang University (China) found that quercetin alleviated liver injury in mice caused by acrylamide, a common contaminant in carbohydrate-rich foods that are processed at high temperatures. The researchers’ analysis showed that quercetin reversed the ferroptosis signaling pathway upregulated by acrylamide.
MOTW update:
December 4, 2023
Quercetin1 was the Molecule of the Week for December 9, 2013. It is an abundant flavonoid in nature. For many years, it has been used to treat conditions ranging from eczema to cancer, with no scientific proof of its effectiveness. Quercetin is found in grapes and is now suspected of causing headaches associated with red wine.
In November, Apramita Devi, Morris Levin, and Andrew L. Waterhouse* at the University of California, Davis, reported that quercetin, which converts to the more bioavailable quercetin-3-glucuronide2 in vivo, inhibits a variant of the mitochondrial enzyme aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH2). Normal ALDH2 eliminates headache-causing acetaldehyde, a metabolite of ethanol; but the dysfunctional variant allows acetaldehyde to accumulate. The authors state that human-subject testing is needed to test their hypothesis.
1. CAS Reg. No. 117-39-5.
2. CAS Reg. No. 22688-79-5.

Learn more about this molecule from CAS, the most authoritative and comprehensive source for chemical information.
Molecule of the Week needs your suggestions!
If your favorite molecule is not in our archive, please send us a message. The molecule can be notable for its current or historical importance or for any quirky reason. Thank you!
Stay Ahead of the Chemistry Curve
Learn how ACS can help you stay ahead in the world of chemistry.

