Lesson 2.5: Changing State—Melting
Accompanying Lesson Plan: Lesson 2.5: Changing State—Melting
Video
Ice Melting on Different Surfaces
- Identical ice cubes are placed on black squares of aluminum and plastic foam.
- Why does one melt faster than the other?
Video
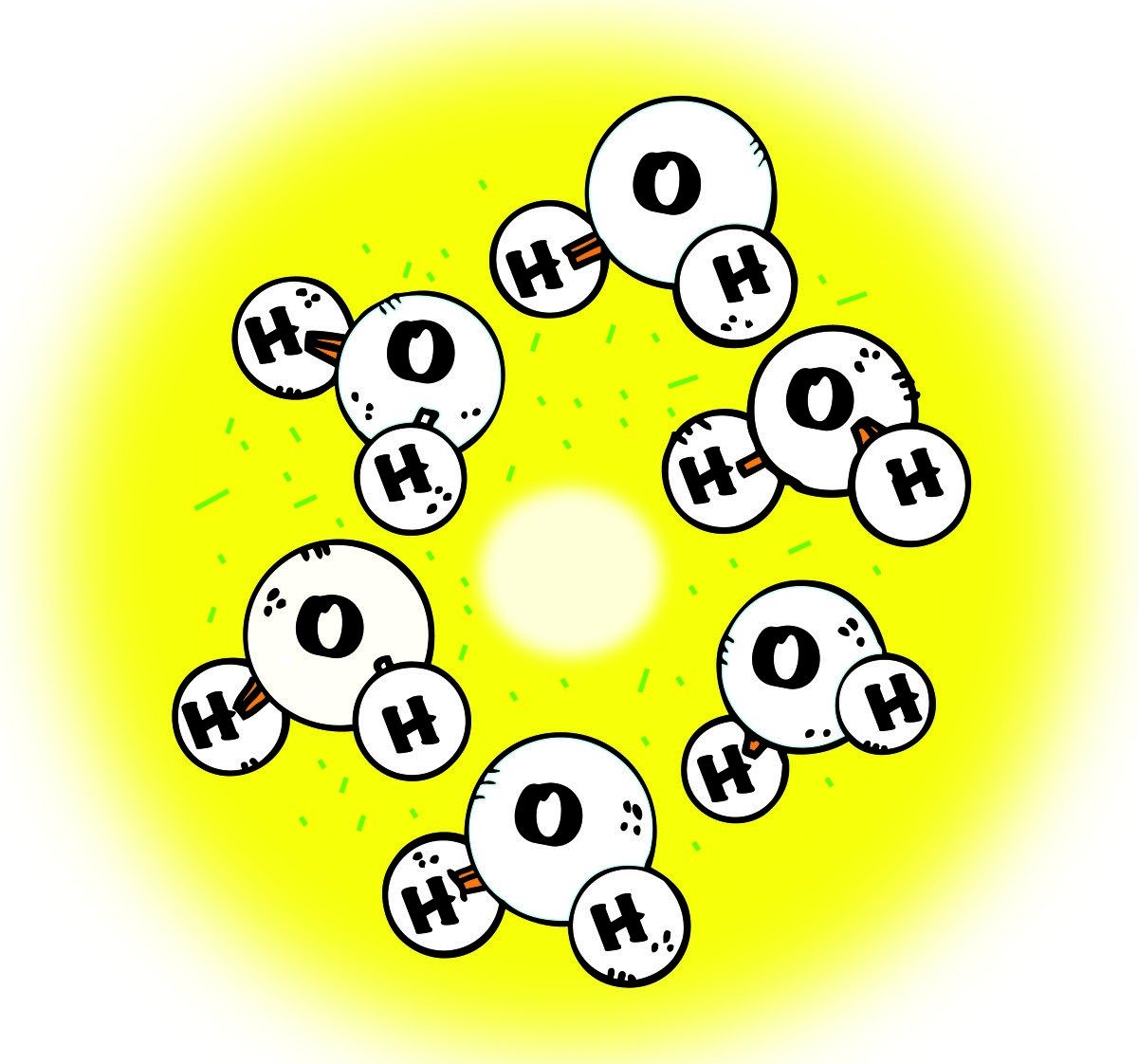
Melting Ice
- As the ice is heated, the motion of the molecules increases.
- Eventually, the motion overcomes the attraction between molecules, and the ice melts and becomes a liquid.
Video used with permission from Roy Tasker, VisChem Project
Image
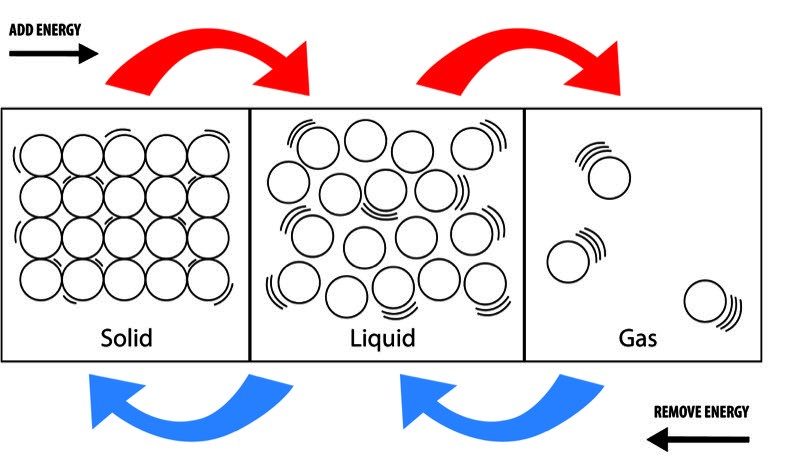
States of Matter
- As energy is added, the motion of the molecules increases and begins to overcome the attractions that molecules have for one another. If enough energy is added, the solid melts to a liquid and the liquid evaporates to a gas.
- As energy is removed, the motion of the molecules decreases and the attractions begin to overcome the motion of the molecules. If enough energy is removed, the gas condenses to a liquid and the liquid freezes to a solid.
Image
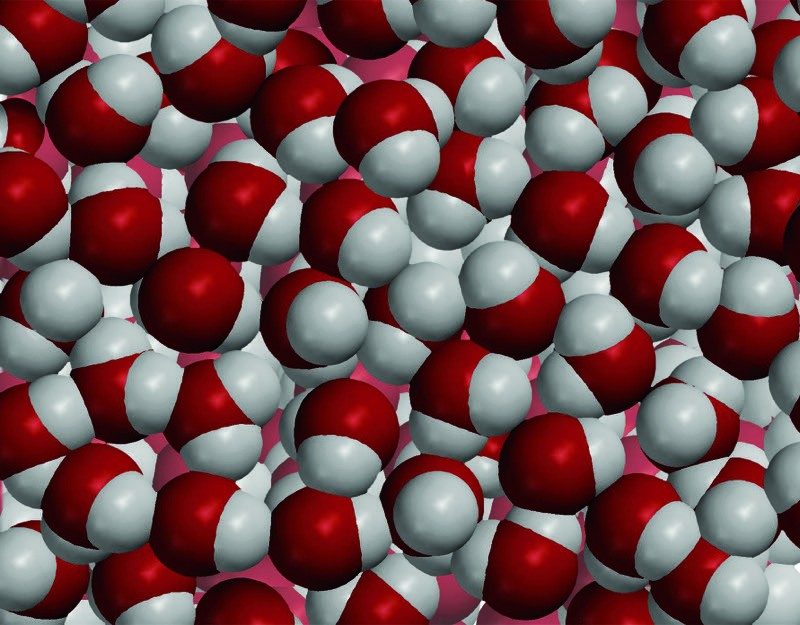
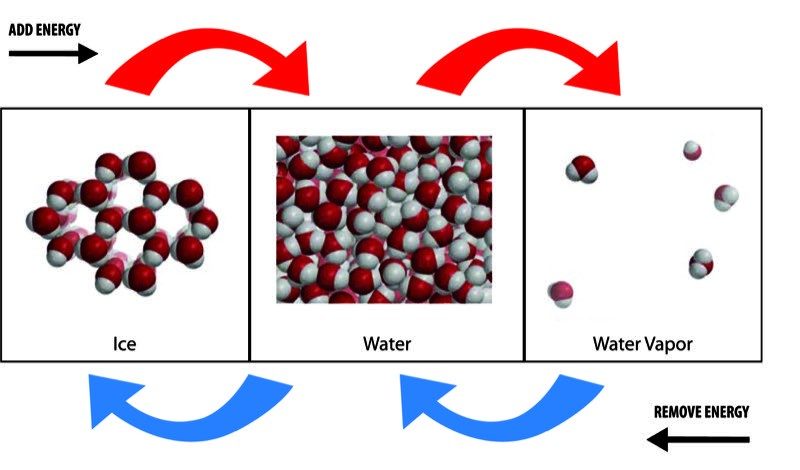
States of Water
- As energy is added, the motion of the water molecules increases and begins to overcome the attractions they have for one another. If enough energy is added, the ice melts to liquid water and the water evaporates to a water vapor.
- As energy is removed, the motion of the molecules decreases and the attractions begin to overcome the motion of the molecules. If enough energy is removed, the water vapor condenses to liquid water and the water freezes to ice.
Image
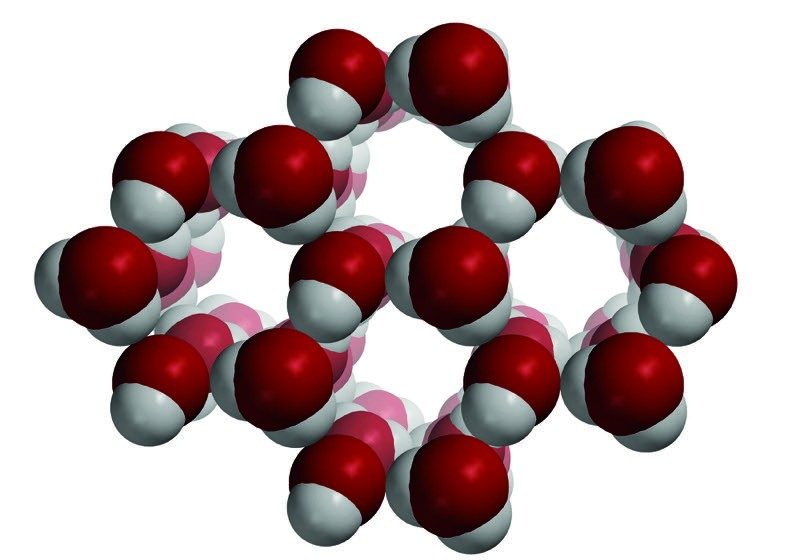
Water Freezes
- When water freezes, the water molecules arrange themselves in a regular hexagonal pattern.
- The hydrogens of one water molecule are near the oxygen atoms of other water molecules.
Video
Dry Ice
- Regular ice melts and leaves a darker wet mark on the paper towel. Dry ice goes directly from a solid to a gas and leaves no mark on the paper towel.
Video
Dry Ice in Water
- When dry ice is placed in water, energy is transferred from the water to the dry ice. This energy causes the dry ice to change state from a solid directly to a gas. This gas is noticeable as the bubbles that form in the water.
Video
Dry Ice in Cold and Hot Water
- The dry ice placed in hot water releases carbon dioxide gas at a faster rate than the dry ice placed in cold water.