Lesson 4.4: Energy Levels, Electrons, and Covalent Bonding
Accompanying Lesson Plan: Lesson 4.4: Energy Levels, Electrons, and Covalent Bonding
Interactive
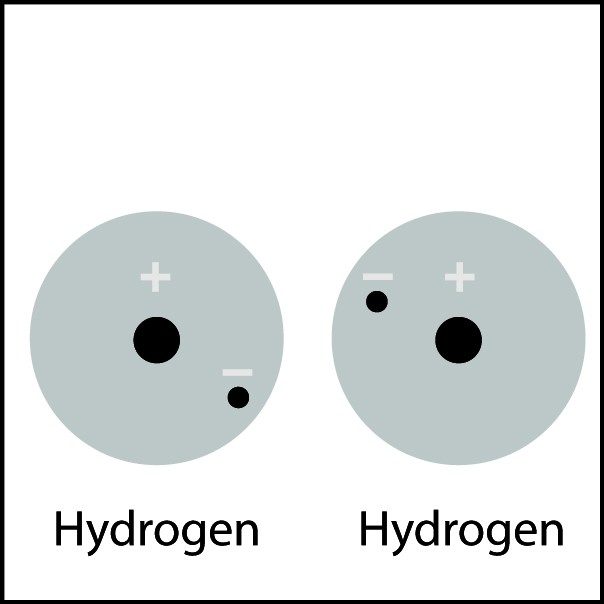
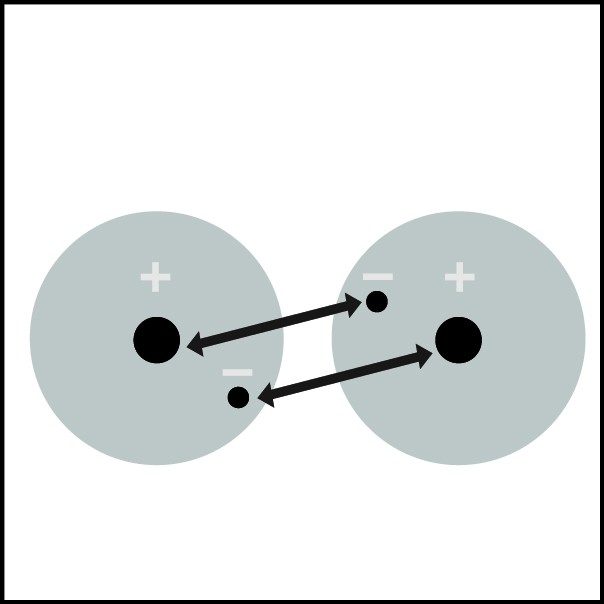
Covalent Bond in Hydrogen
- When two hydrogen atoms get close enough, the electron from each atom feels an attraction from the proton in the other atom's nucleus.
- This attraction pulls the atoms together.
- The electrons end up being shared by the atoms in a region around the nucleus of both atoms.
Image
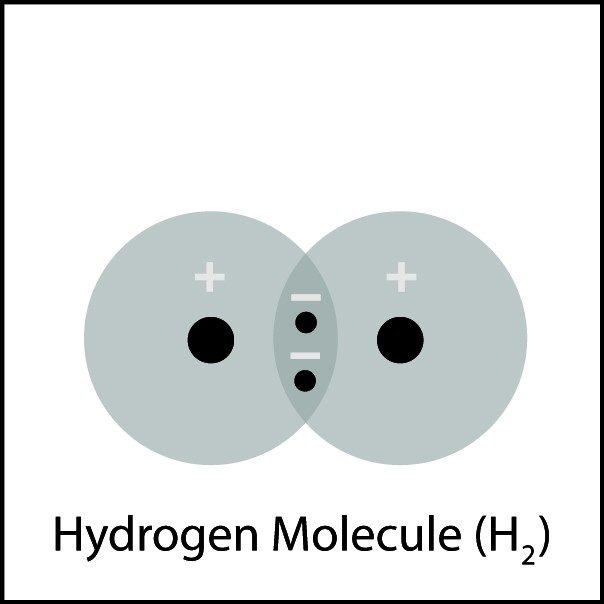
Covalent Bonding in Hydrogen 2
- Hydrogen atoms are close together. The electron from each atom feels the attraction from the proton in the nucleus of the other atom.
- This attraction pulls the atoms together and the electrons are shared by both atoms.
- The atoms bond because there is a strong enough attraction in both directions and room for the electrons in the outer energy level of the atoms.
Interactive
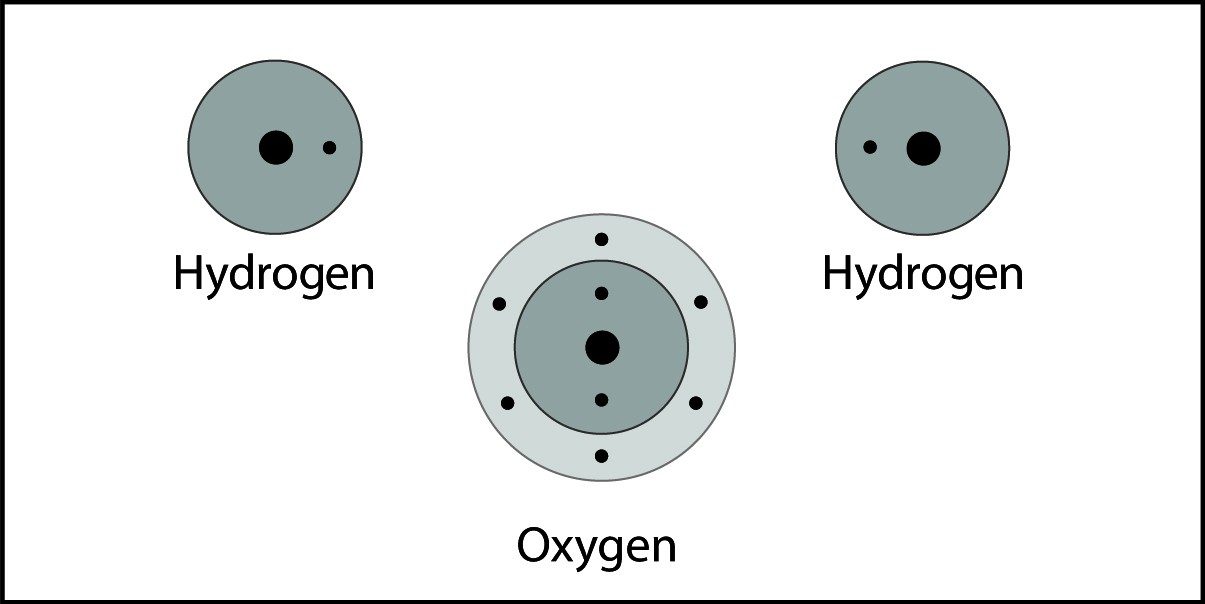
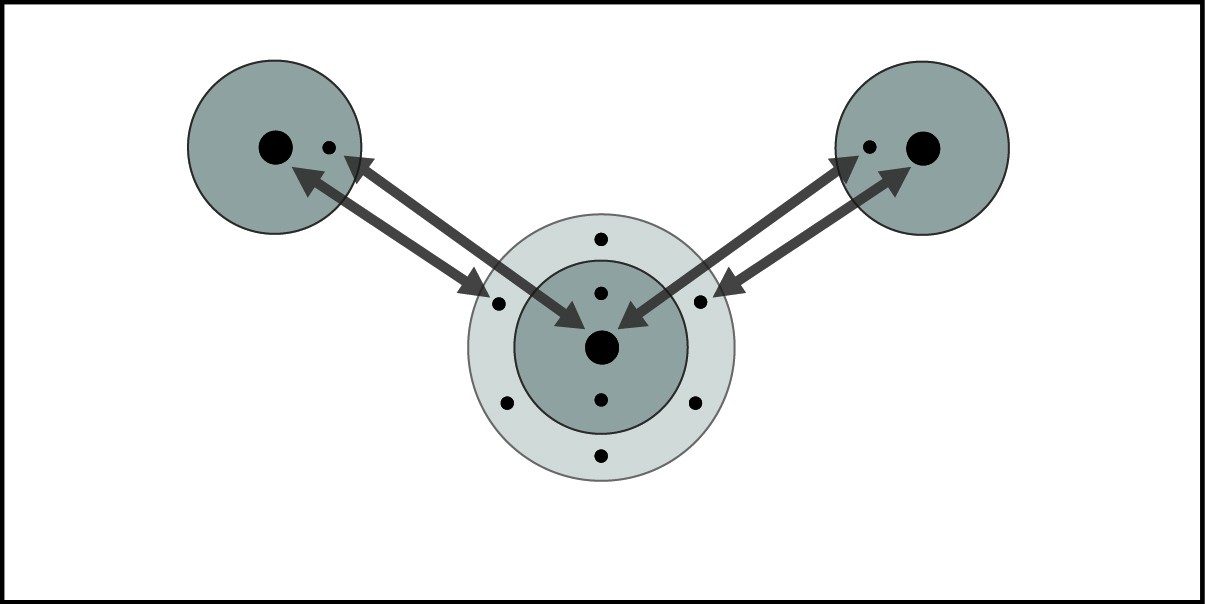
Covalent Bond in Water
- When two hydrogen atoms and an oxygen atom get close enough, the electron from each atom feels an attraction from the protons in the other atom's nucleus.
- This attraction pulls the atoms together.
- The electrons end up being shared by the atoms in a region around the nucleus of both atoms.
Image
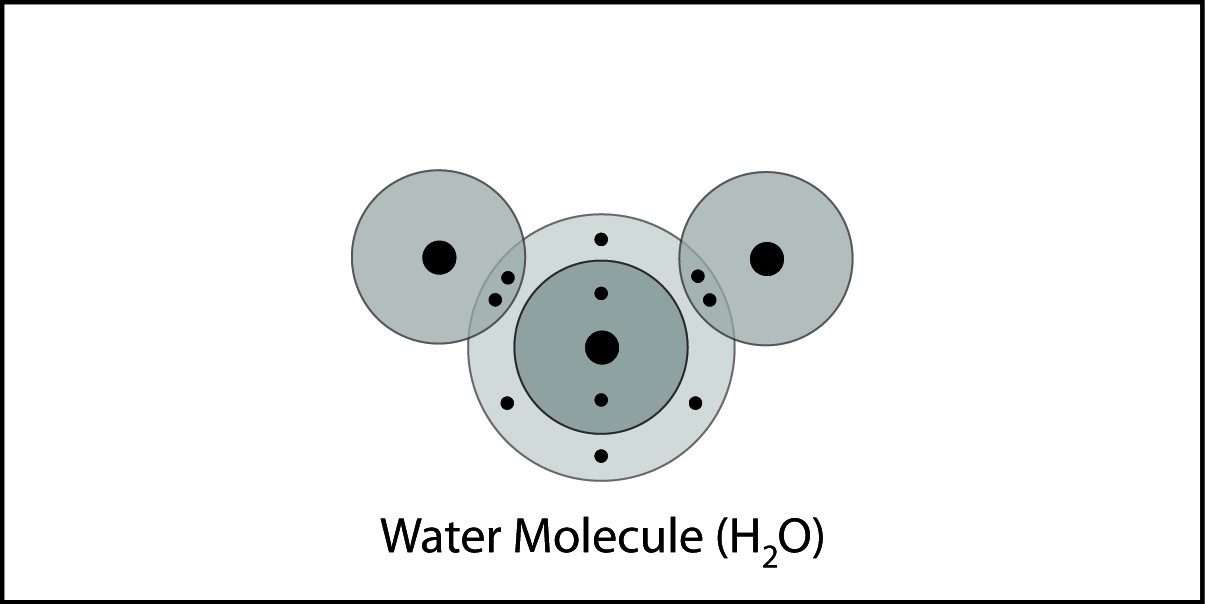
Covalent Bonding in Water 2
- Hydrogen atoms and an oxygen atom are close together.
- Electrons from each atom feel the attraction from the protons in the nucleus of the other atom.
- This attraction pulls the atoms together and the electrons are shared by both atoms.
- The atoms bond because there is a strong enough attraction in both directions and room for the electrons in the outer energy level of the atoms.
Video
Electrolysis
- Electricity causes the rearrangement of electrons and atoms from water molecules.
- Two hydrogen atoms covalently bond to form hydrogen gas.
- Two oxygen atoms covalently bond to form oxygen gas.
- There are twice as many hydrogen atoms as oxygen atoms so more hydrogen gas is formed.
Interactive
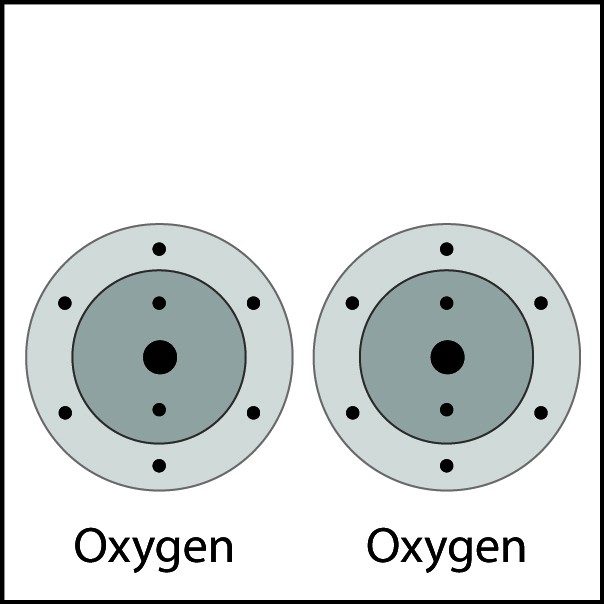
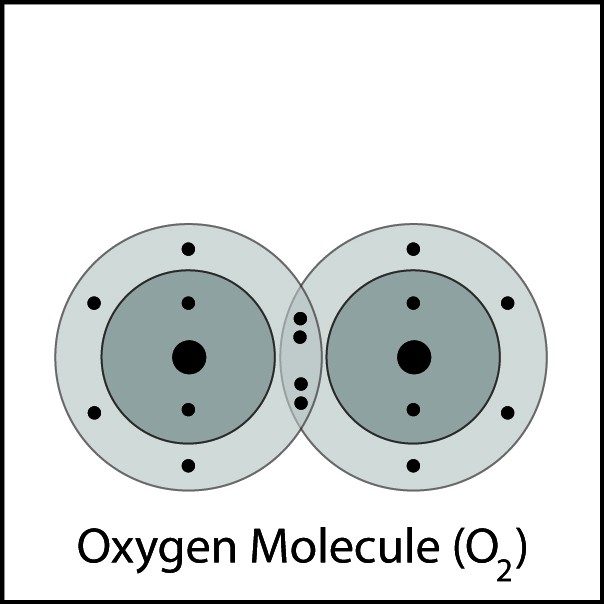
Oxygen's Double Bond
- Oxygen atoms are close together.
- The electrons from each atom feel the attraction from the protons in the nucleus of the other atom.
- This attraction pulls the atoms together and the electrons are shared by both atoms.
- The atoms form a double bond because there is a strong enough attraction in both directions and room for the electrons in the outer energy level of the atoms.
Image
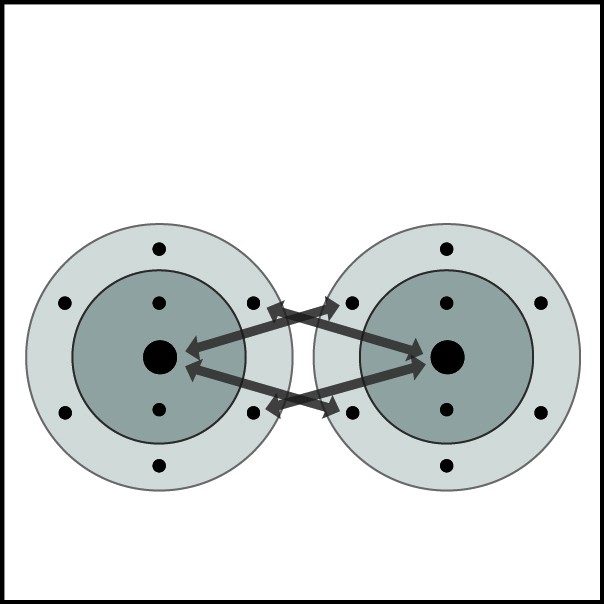
Oxygens Double Bond 2
- Oxygen atoms are close together.
- The electrons from each atom feel the attraction from the protons in the nucleus of the other atom.
- This attraction pulls the atoms together and the electrons are shared by both atoms.
- The atoms form a double bond because there is a strong enough attraction in both directions and room for the electrons in the outer energy level of the atoms.
Image
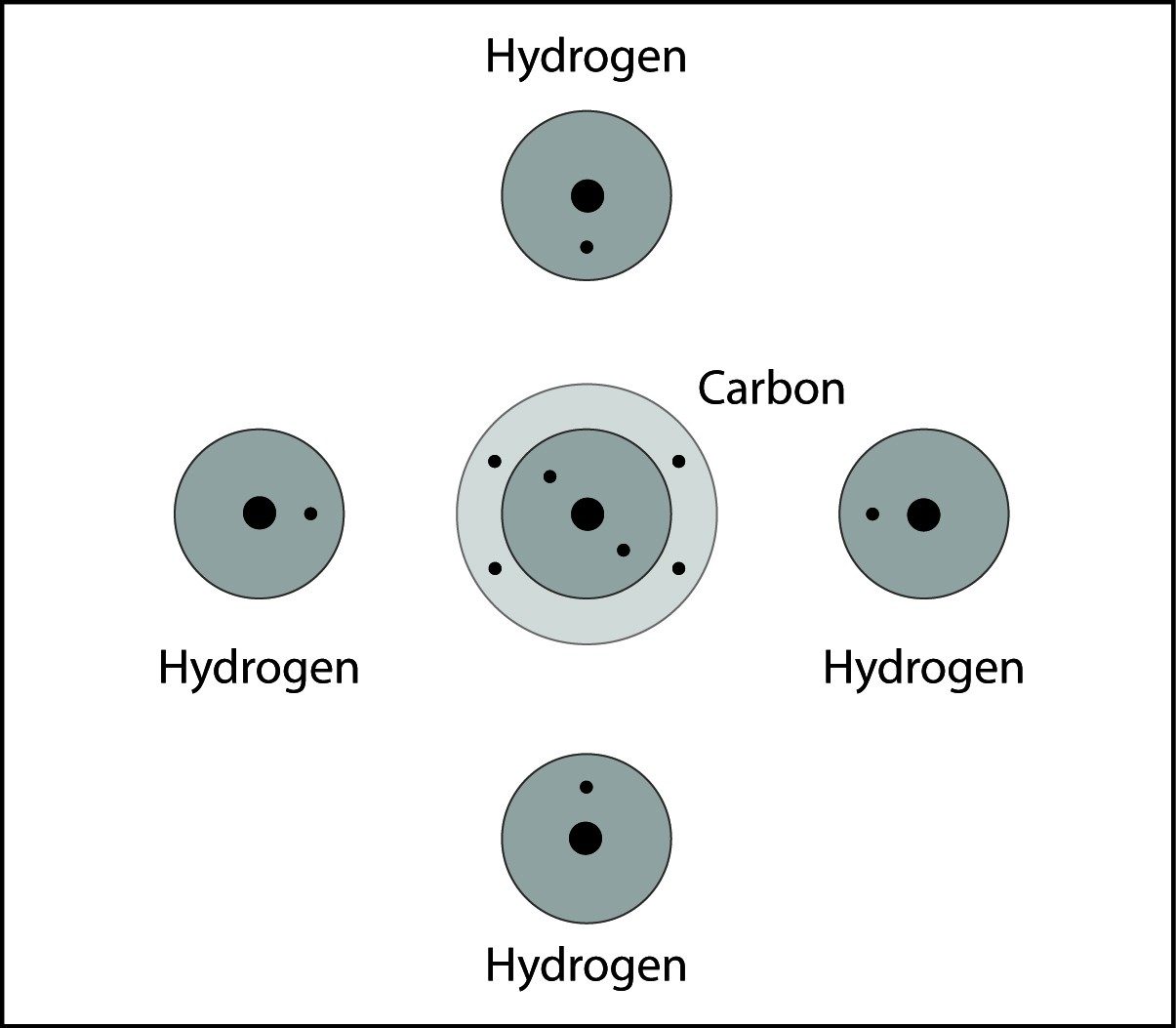
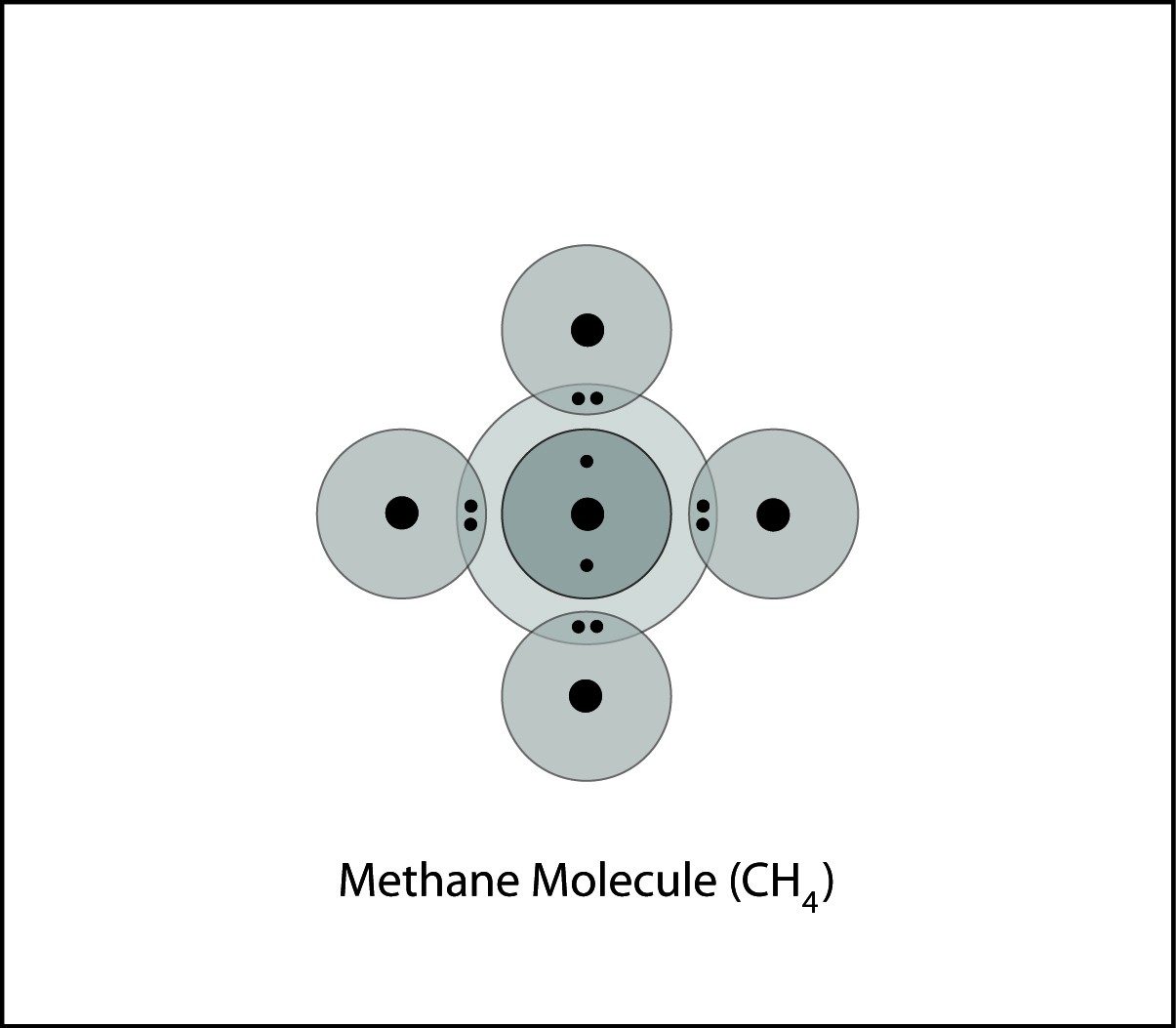
Covalent Bonding in Methane
- The carbon atom and hydrogen atoms are close together.
- The electrons from each atom feels the attraction from the proton in the nucleus of the other atom.
- This attraction pulls the atoms together and the electrons are shared by both atoms.
- The atoms bond because there is a strong enough attraction in both directions and room for the electrons in the outer energy level of the atoms.
Image
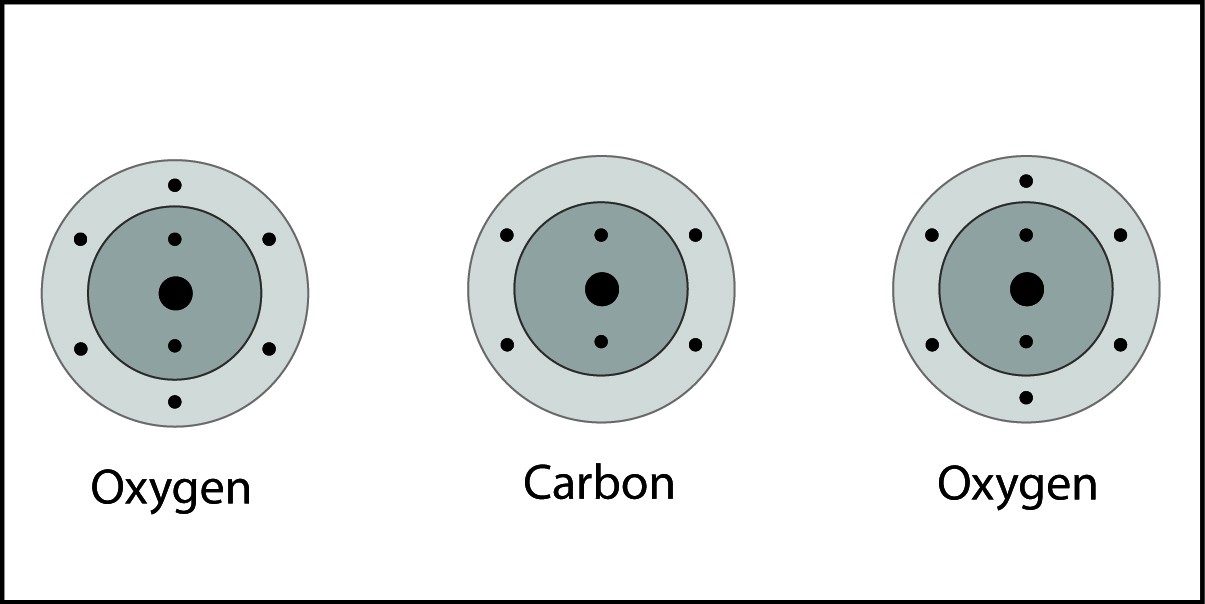
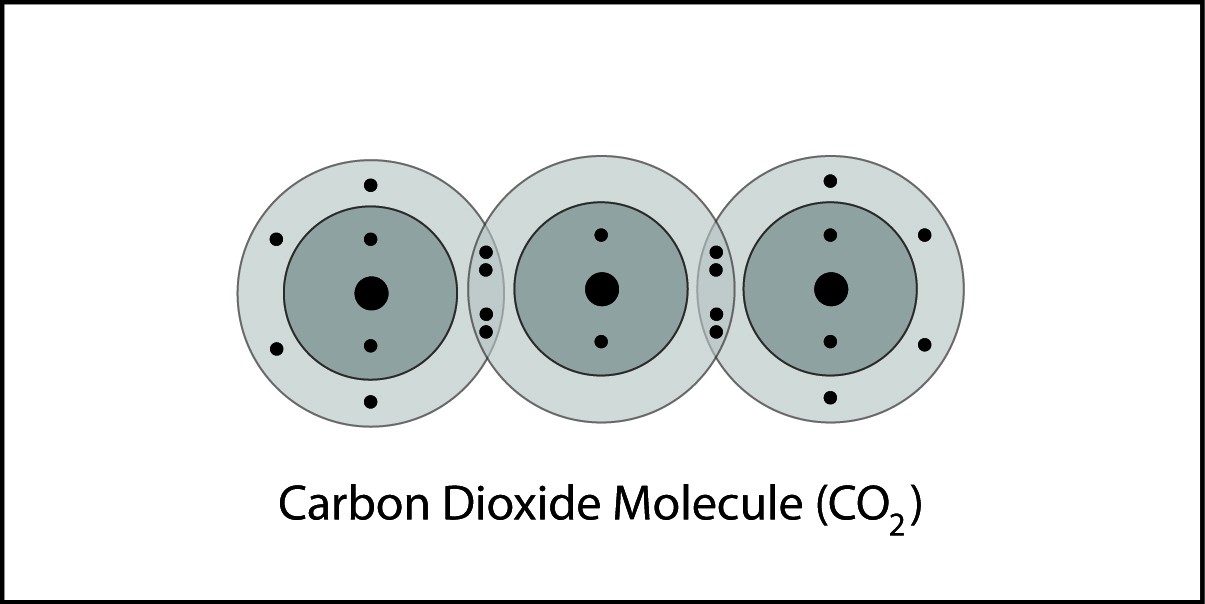
Covalent Bonding in Carbon Dioxide
- A carbon atom and two oxygen atoms are close together.
- The electrons from each atom feel the attraction from the protons in the nucleus of the other atom.
- This attraction pulls the atoms together and the electrons are shared by both atoms.
- The atoms form a double bond because there is a strong enough attraction in both directions and room for the electrons in the outer energy level of the atoms.