Lesson 4.5: Energy Levels, Electrons, and Ionic Bonding
Accompanying Lesson Plan: Lesson 4.5: Energy Levels, Electrons, and Ionic Bonding
Video
Sodium and Chlorine React
- A small piece of sodium metal is placed in a flask of chlorine gas.
- A little water helps expose the sodium so it can react with the chlorine gas.
- The reaction releases a lot of heat as the ionic compound sodium chloride is formed.
The demonstration shown in this video is very dangerous. Do not attempt to perform this demonstration.
Video used with permission from Chemical Education Exchange (ChemEd X)
Interactive
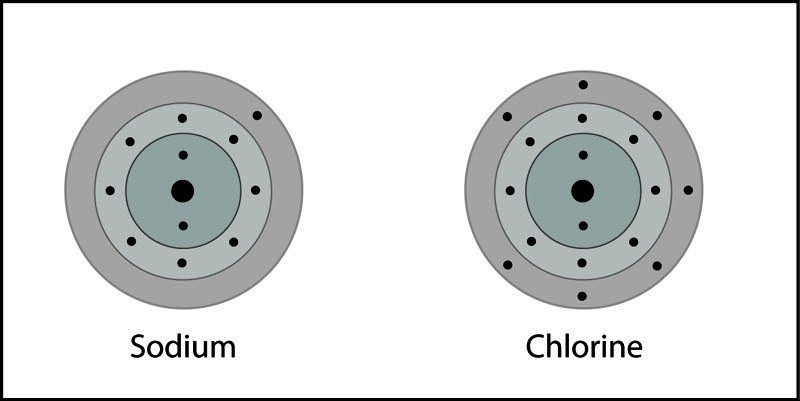
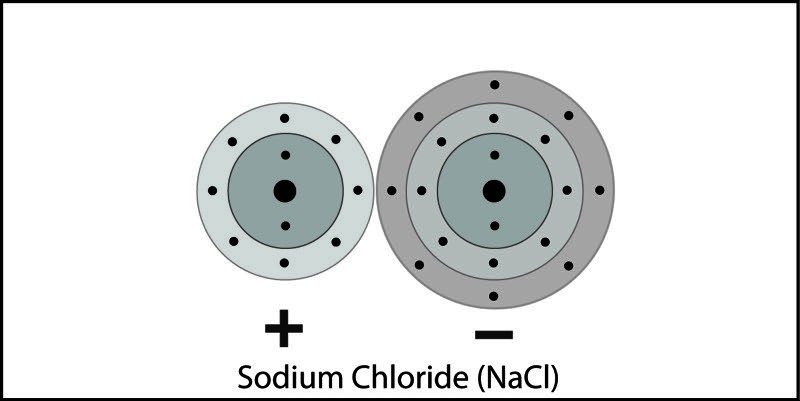
Ionic Bond in Sodium Chloride
- A sodium and chlorine atom are near each other.
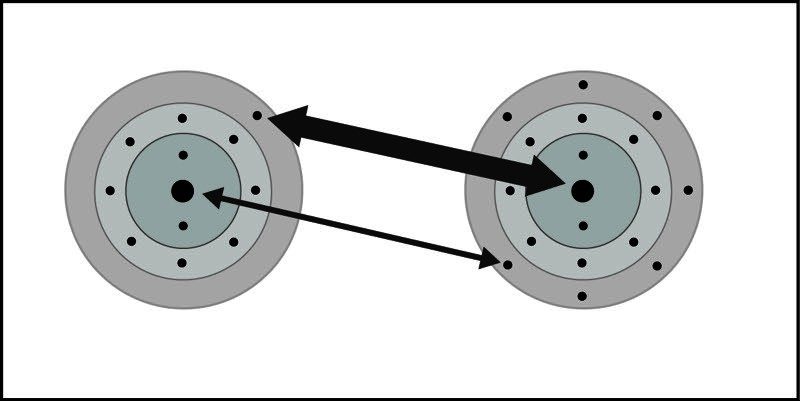
- An electron from each atom feels the attraction from the other atom's nucleus.
- The attraction by chlorine is stronger than the attraction by sodium.
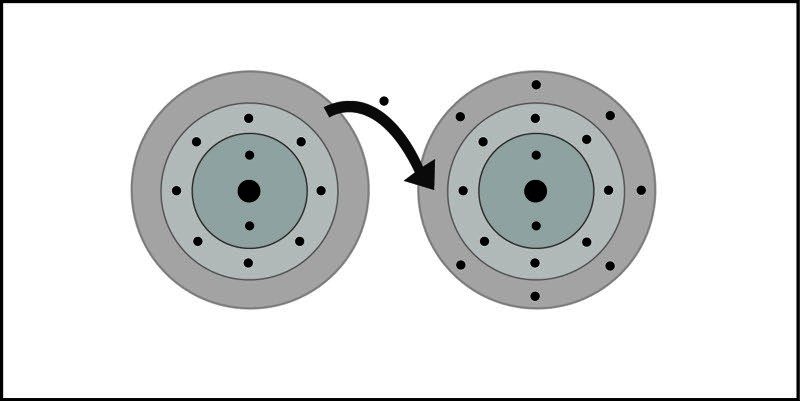
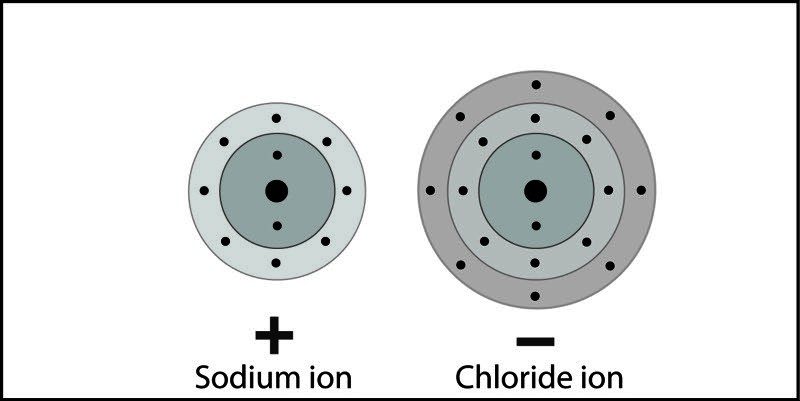
- An electron is transferred from sodium to chlorine. Sodium becomes a positive ion and chlorine becomes a negative ion.
- The positive and negative ions attract each other and form the ionic compound sodium chloride.
Image
Ionic Bond in Sodium Chloride 2
- A sodium and chlorine atom are near each other.
- An electron from each atom feels the attraction from the other atom's nucleus.
- The attraction by chlorine is stronger than the attraction by sodium.
- An electron is transferred from sodium to chlorine. Sodium becomes a positive ion and chlorine becomes a negative ion.
- The positive and negative ions attract each other and form the ionic compound sodium chloride.
Video
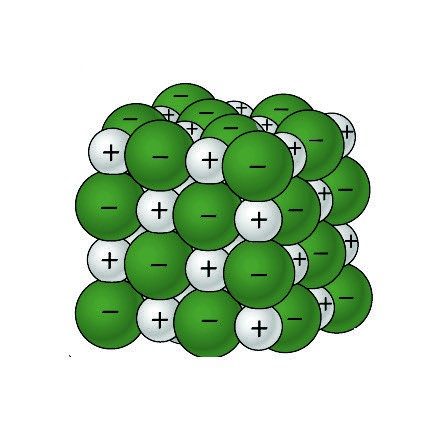
Sodium Chloride Crystal
- The sodium chloride crystal is made up of alternating sodium and chloride ions.
Video used with permission from Roy Tasker, VisChem Project
Image
Cubic Sodium Chloride
- When salt crystals are examined closely under a microscope, their cubic shape becomes clear.
Interactive
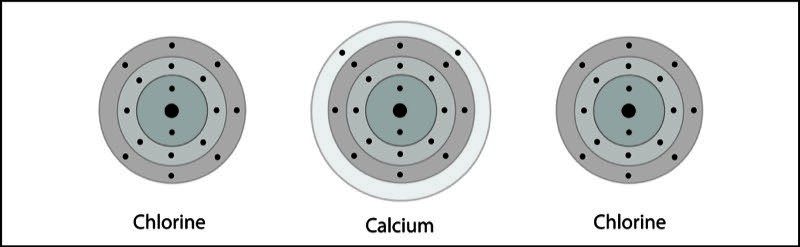
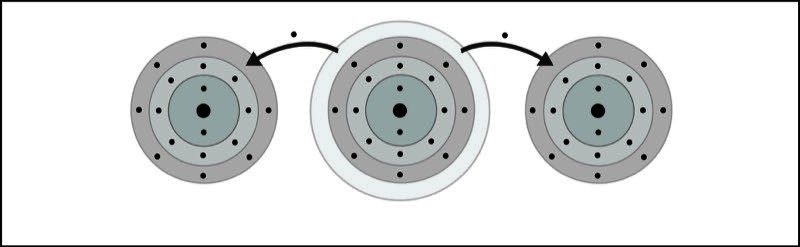
Calcium Chloride Ionic Bond
- One calcium and two chlorine atoms are near each other.
- An electron from each atom feels the attraction from the other atom's nucleus.
- The attraction by the chlorine atoms is stronger than the attraction by the calcium atom.
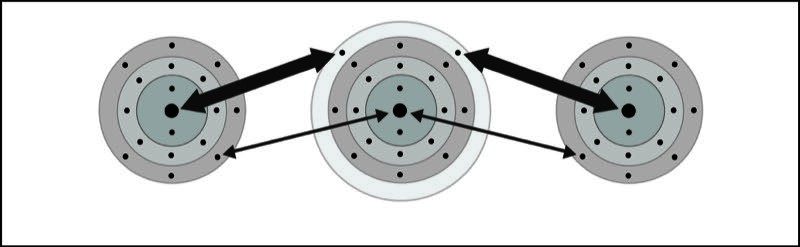
- Two electrons are transferred from the calcium atom, one to each chlorine atom.
- Calcium becomes a +2 ion and each chlorine becomes a -1 ion. The +2 calcium ion and the two -1 chloride ions attract each other and form an ionic bond and the compound calcium chloride.
Image
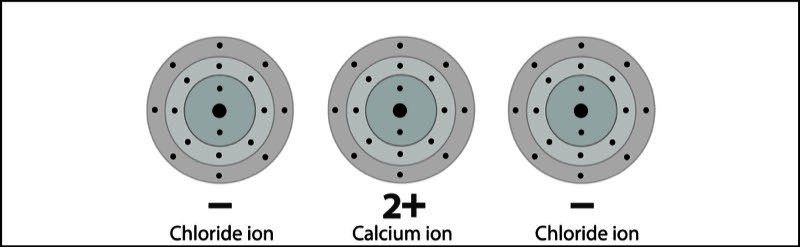
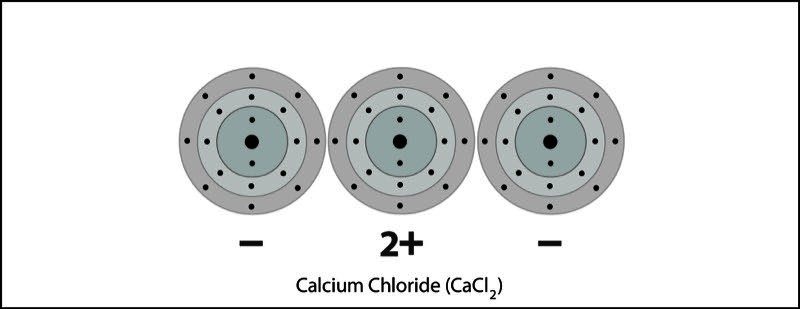
Calcium Chloride Ionic Bond 2
- One calcium and two chlorine atoms are near each other.
- An electron from each atom feels the attraction from the other atom's nucleus.
- The attraction by the chlorine atoms is stronger than the attraction by the calcium atom.
- Two electrons are transferred from the calcium atom, one to each chlorine atom.
- Calcium becomes a +2 ion and each chlorine becomes a -1 ion. The +2 calcium ion and the two -1 chloride ions attract each other and form an ionic bond and the compound calcium chloride.